Page 648 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 648
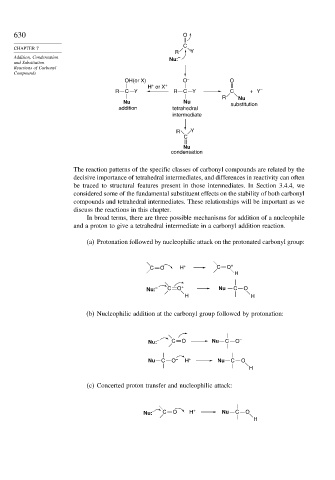
630 O
C
CHAPTER 7
R Y
Addition, Condensation Nu: –
and Substitution
Reactions of Carbonyl
Compounds
OH(or X) O – O
+
H or X +
R C Y R C Y C + Y –
R Nu
Nu Nu substitution
addition tetrahedral
intermediate
R Y
C
Nu
condensation
The reaction patterns of the specific classes of carbonyl compounds are related by the
decisive importance of tetrahedral intermediates, and differences in reactivity can often
be traced to structural features present in those intermediates. In Section 3.4.4, we
considered some of the fundamental substituent effects on the stability of both carbonyl
compounds and tetrahedral intermediates. These relationships will be important as we
discuss the reactions in this chapter.
In broad terms, there are three possible mechanisms for addition of a nucleophile
and a proton to give a tetrahedral intermediate in a carbonyl addition reaction.
(a) Protonation followed by nucleophilic attack on the protonated carbonyl group:
C O H + C O +
H
Nu: – C O + Nu C O
H H
(b) Nucleophilic addition at the carbonyl group followed by protonation:
Nu: – C O Nu C O –
Nu C O – H + Nu C O
H
(c) Concerted proton transfer and nucleophilic attack:
Nu: – C O H + Nu C O
H