Page 687 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 687
669
1.6
SECTION 7.5
1.4
Intramolecular Catalysis
1.2 of Carbonyl Substitution
Reactions
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
pH
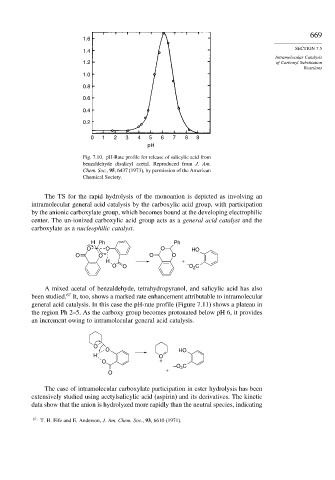
Fig. 7.10. pH-Rate profile for release of salicylic acid from
benzaldehyde disalicyl acetal. Reproduced from J. Am.
Chem. Soc., 95, 6437 (1973), by permission of the American
Chemical Society.
The TS for the rapid hydrolysis of the monoanion is depicted as involving an
intramolecular general acid catalysis by the carboxylic acid group, with participation
by the anionic carboxylate group, which becomes bound at the developing electrophilic
center. The un-ionized carboxylic acid group acts as a general acid catalyst and the
carboxylate as a nucleophilic catalyst.
H Ph Ph
O O O HO
O O O O
H +
O O – O C
2
A mixed acetal of benzaldehyde, tetrahydropyranol, and salicylic acid has also
67
been studied. It, too, shows a marked rate enhancement attributable to intramolecular
general acid catalysis. In this case the pH-rate profile (Figure 7.11) shows a plateau in
the region Ph 2–5. As the carboxy group becomes protonated below pH 6, it provides
an increment owing to intramolecular general acid catalysis.
O
O HO
H O
O +
–O 2 C
+
O
The case of intramolecular carboxylate participation in ester hydrolysis has been
extensively studied using acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) and its derivatives. The kinetic
data show that the anion is hydrolyzed more rapidly than the neutral species, indicating
67
T. H. Fife and E. Anderson, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 93, 6610 (1971).