Page 691 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 691
4
dominant. Analysis of the kinetic data indicates an acceleration of about 10 . Although 673
the nucleophilic catalysis mechanism was not observed in the parent compound, it did
occur in certain substituted derivatives. SECTION 7.5
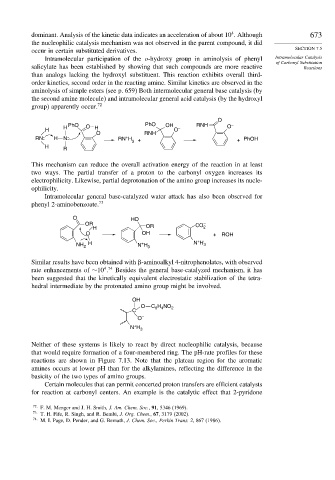
Intramolecular participation of the o-hydroxy group in aminolysis of phenyl Intramolecular Catalysis
of Carbonyl Substitution
salicylate has been established by showing that such compounds are more reactive Reactions
than analogs lacking the hydroxyl substituent. This reaction exhibits overall third-
order kinetics, second order in the reacting amine. Similar kinetics are observed in the
aminolysis of simple esters (see p. 659) Both intermolecular general base catalysis (by
the second amine molecule) and intramolecular general acid catalysis (by the hydroxyl
group) apparently occur. 72
O
PhO PhO OH RNH –
H O H – O
H O
O RNH
RN: H N: RN H 3 + + PhOH
+
H R
This mechanism can reduce the overall activation energy of the reaction in at least
two ways. The partial transfer of a proton to the carbonyl oxygen increases its
electrophilicity. Likewise, partial deprotonation of the amino group increases its nucle-
ophilicity.
Intramolecular general base-catalyzed water attack has also been observed for
phenyl 2-aminobenzoate. 73
O HO
OR CO –
H OR 2
O OH + ROH
+
H + N H 3
NH 2 N H 3
Similar results have been obtained with -aminoalkyl 4-nitrophenolates, with observed
4 74
rate enhancements of ∼10 . Besides the general base-catalyzed mechanism, it has
been suggested that the kinetically equivalent electrostatic stabilization of the tetra-
hedral intermediate by the protonated amino group might be involved.
OH
O C H NO
C 6 4 2
O –
+
N H 3
Neither of these systems is likely to react by direct nucleophilic catalysis, because
that would require formation of a four-membered ring. The pH-rate profiles for these
reactions are shown in Figure 7.13. Note that the plateau region for the aromatic
amines occurs at lower pH than for the alkylamines, reflecting the difference in the
basicity of the two types of amino groups.
Certain molecules that can permit concerted proton transfers are efficient catalysts
for reaction at carbonyl centers. An example is the catalytic effect that 2-pyridone
72
F. M. Menger and J. H. Smith, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 91, 5346 (1969).
73 T. H. Fife, R. Singh, and R. Bembi, J. Org. Chem., 67, 3179 (2002).
74
M. I. Page, D. Pender, and G. Bernath, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 867 (1986).