Page 694 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 694
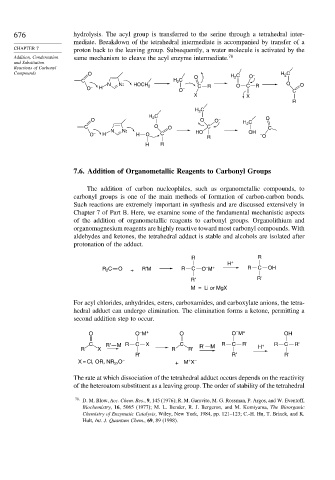
676 hydrolysis. The acyl group is transferred to the serine through a tetrahedral inter-
mediate. Breakdown of the tetrahedral intermediate is accompanied by transfer of a
CHAPTER 7 proton back to the leaving group. Subsequently, a water molecule is activated by the
Addition, Condensation same mechanism to cleave the acyl enzyme intermediate. 78
and Substitution
Reactions of Carbonyl
Compounds O – H C
O H C O 2
2
C H C
2
N N: HOCH O C R O O
O – H 2 O – C R C
X X
R
H C
2
H C
O 2 O O – O
H 2 C
C O O C C
N N: HO OH
O – H H O C –
R O
H R
7.6. Addition of Organometallic Reagents to Carbonyl Groups
The addition of carbon nucleophiles, such as organometallic compounds, to
carbonyl groups is one of the main methods of formation of carbon-carbon bonds.
Such reactions are extremely important in synthesis and are discussed extensively in
Chapter 7 of Part B. Here, we examine some of the fundamental mechanistic aspects
of the addition of organometallic reagents to carbonyl groups. Organolithium and
organomagnesium reagents are highly reactive toward most carbonyl compounds. With
aldehydes and ketones, the tetrahedral adduct is stable and alcohols are isolated after
protonation of the adduct.
R R
H +
–
R 2 C O + R'M R C O M + R C OH
R' R'
M = Li or MgX
For acyl chlorides, anhydrides, esters, carboxamides, and carboxylate anions, the tetra-
hedral adduct can undergo elimination. The elimination forms a ketone, permitting a
second addition step to occur.
–
–
O O M + O O M + OH
C R' M R C X C R' M R C R' + R C R'
R X R R' H
R' R' R'
+ –
X = Cl, OR, NR ,O – + M X
2
The rate at which dissociation of the tetrahedral adduct occurs depends on the reactivity
of the heteroatom substituent as a leaving group. The order of stability of the tetrahedral
78
D. M. Blow, Acc. Chem. Res., 9, 145 (1976); R. M. Garavito, M. G. Rossman, P. Argos, and W. Eventoff,
Biochemistry, 16, 5065 (1977); M. L. Bender, R. J. Bergeron, and M. Komiyama, The Bioorganic
Chemistry of Enzymatic Catalysis, Wiley, New York, 1984, pp. 121–123; C.-H. Hu, T. Brinck, and K.
Hult, Int. J. Quantum Chem., 69, 89 (1998).