Page 79 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 79
58
CHAPTER 1
Chemical Bonding
and Molecular Structure
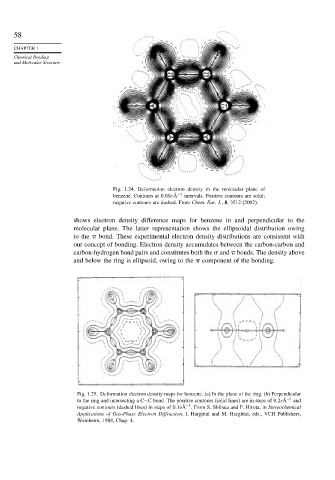
Fig. 1.24. Deformation electron density in the molecular plane of
benzene. Contours at 0 05eÅ −3 intervals. Positive contours are solid;
negative contours are dashed. From Chem. Eur. J., 8, 3512 (2002).
shows electron density difference maps for benzene in and perpendicular to the
molecular plane. The latter representation shows the ellipsoidal distribution owing
to the bond. These experimental electron density distributions are consistent with
our concept of bonding. Electron density accumulates between the carbon-carbon and
carbon-hydrogen bond pairs and constitutes both the and bonds. The density above
and below the ring is ellipsoid, owing to the component of the bonding.
Fig. 1.25. Deformation electron density maps for benzene. (a) In the plane of the ring. (b) Perpendicular
to the ring and intersecting a C−C bond. The positive contours (solid lines) are in steps of 0 2eÅ −3 and
−3
negative contours (dashed lines) in steps of 0 1eÅ . From S. Shibata and F. Hirota, in Stereochemical
Applications of Gas-Phase Electron Diffraction, I. Hargittai and M. Hargittai, eds., VCH Publishers,
Weinheim, 1988, Chap. 4.