Page 827 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 827
810
CHAPTER 9
Aromatic Substitution
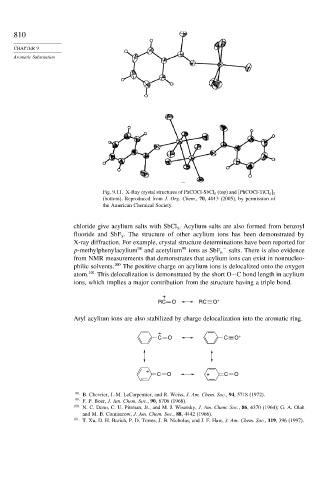
Fig. 9.11. X-Ray crystal structures of PhCOCl-SbCl 5 (top) and [PhCOCl-TiCl 4 ] 2
(bottom). Reproduced from J. Org. Chem., 70, 4013 (2005), by permission of
the American Chemical Society.
chloride give acylium salts with SbCl . Acylium salts are also formed from benzoyl
5
fluoride and SbF . The structure of other acylium ions has been demonstrated by
5
X-ray diffraction. For example, crystal structure determinations have been reported for
p-methylphenylacylium 98 and acetylium 99 ions as SbF 6 − salts. There is also evidence
from NMR measurements that demonstrates that acylium ions can exist in nonnucleo-
philic solvents. 100 The positive charge on acylium ions is delocalized onto the oxygen
atom. 101 This delocalization is demonstrated by the short O−C bond length in acylium
ions, which implies a major contribution from the structure having a triple bond.
+
RC O RC O +
Aryl acylium ions are also stabilized by charge delocalization into the aromatic ring.
+
C O C O +
+
C O + C O
98 B. Chevrier, J.-M. LeCarpentier, and R. Weiss, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 94, 5718 (1972).
99
F. P. Boer, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 90, 6706 (1968).
100 N. C. Deno, C. U. Pittman, Jr., and M. J. Wisotsky, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 86, 4370 (1964); G. A. Olah
and M. B. Comisarow, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 88, 4442 (1966).
101
T. Xu, D. H. Barich, P. D. Torres, J. B. Nicholas, and J. F. Haw, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 119, 396 (1997).