Page 100 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 100
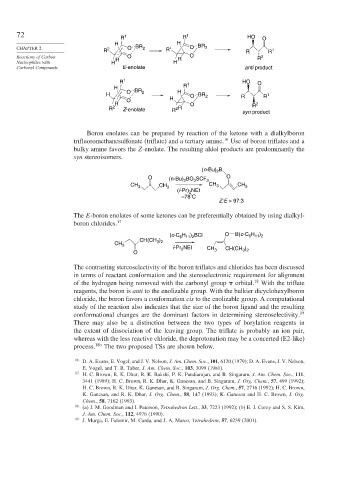
72 R 1 R 1 HO O
H H
CHAPTER 2 2 O BR 2 R′ O BR 2
R R R 1
Reactions of Carbon R O R O R 2
Nucleophiles with H H
Carbonyl Compounds E-enolate anti product
R 1 1 HO O
H R
O BR 2 H
H O BR 2 R R 1
H
O
R O R 2
R 2 Z-enolate R 2 R syn product
Boron enolates can be prepared by reaction of the ketone with a dialkylboron
16
trifluoromethanesulfonate (triflate) and a tertiary amine. Use of boron triflates and a
bulky amine favors the Z-enolate. The resulting aldol products are predominantly the
syn stereoisomers.
(n-Bu) B
2
O (n-Bu) BO SCF 3 O
2
3
CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 CH 3
(i-Pr) NEt
2
°
–78 C
Z:E > 97:3
The E-boron enolates of some ketones can be preferentially obtained by using dialkyl-
boron chlorides. 17
(c-C H ) BCl O B(c-C H )
6 11 2
6 11 2
)
CH(CH 3 2
CH 3
i-Pr 2 NEt CH 3 CH(CH )
3 2
O
The contrasting stereoselectivity of the boron triflates and chlorides has been discussed
in terms of reactant conformation and the stereoelectronic requirement for alignment
of the hydrogen being removed with the carbonyl group orbital. 18 With the triflate
reagents, the boron is anti to the enolizable group. With the bulkier dicyclohexylboron
chloride, the boron favors a conformation cis to the enolizable group. A computational
study of the reaction also indicates that the size of the boron ligand and the resulting
conformational changes are the dominant factors in determining stereoselectivity. 19
There may also be a distinction between the two types of borylation reagents in
the extent of dissociation of the leaving group. The triflate is probably an ion pair,
whereas with the less reactive chloride, the deprotonation may be a concerted (E2-like)
process. 18b The two proposed TSs are shown below.
16 D. A. Evans, E. Vogel, and J. V. Nelson, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 101, 6120 (1979); D. A. Evans, J. V. Nelson,
E. Vogel, and T. R. Taber, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 103, 3099 (1981).
17
H. C. Brown, R. K. Dhar, R. K. Bakshi, P. K. Pandiarajan, and B. Singaram, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 111,
3441 (1989); H. C. Brown, R. K. Dhar, K. Ganesan, and B. Singaram, J. Org. Chem., 57, 499 (1992);
H. C. Brown, R. K. Dhar, K. Ganesan, and B. Singaram, J. Org. Chem., 57, 2716 (1992); H. C. Brown,
K. Ganesan, and R. K. Dhar, J. Org. Chem., 58, 147 (1993); K. Ganesan and H. C. Brown, J. Org.
Chem., 58, 7162 (1993).
18 (a) J. M. Goodman and I. Paterson, Tetrahedron Lett., 33, 7223 (1992); (b) E. J. Corey and S. S. Kim,
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 112, 4976 (1990).
19
J. Murga, E. Falomir, M. Carda, and J. A. Marco, Tetrahedron, 57, 6239 (2001).