Page 1270 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 1270
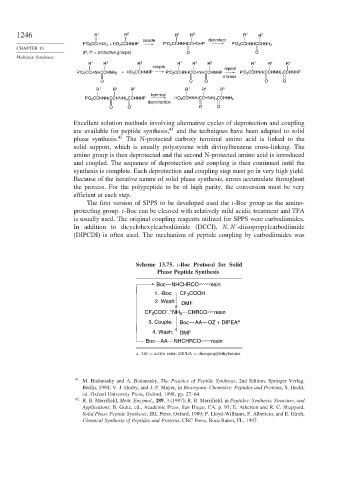
1246 R 1 R 2 R 1 R 2 R 1 R 2
couple deprotect
P′O 2 CCHNH 2 + HO 2 CCHNHP P′O 2 CCHNHCCHNHP P′O 2 CCHNHCCHNH 2
CHAPTER 13
(P, P′ = protective groups) O O
Multistep Syntheses
R 1 R 2 R 3 R 1 R 2 R 3 R 1 R x R n
couple repeat
+ HO 2 CCHNHP P′O 2 CCHNHCCHNHCCHNHP P′O 2 CCHNH(CCHNH) x CCHNHP
P′O 2 CCHNHCCHNH 2
n times
O O O O O
R 1 R x R n R 1 R x R n
terminal
P′O 2 CCHNH(CCHNH) x CCHNHP HO 2 CCHNH(CCHNH) x CCHNH 2
deprotection
O O O O
Excellent solution methods involving alternative cycles of deprotection and coupling
are available for peptide synthesis, 41 and the techniques have been adapted to solid
phase synthesis. 42 The N-protected carboxy terminal amino acid is linked to the
solid support, which is usually polystyrene with divinylbenzene cross-linking. The
amino group is then deprotected and the second N-protected amino acid is introduced
and coupled. The sequence of deprotection and coupling is then continued until the
synthesis is complete. Each deprotection and coupling step must go in very high yield.
Because of the iterative nature of solid phase synthesis, errors accumulate throughout
the process. For the polypeptide to be of high purity, the conversion must be very
efficient at each step.
The first version of SPPS to be developed used the t-Boc group as the amino-
protecting group. t-Boc can be cleaved with relatively mild acidic treatment and TFA
is usually used. The original coupling reagents utilized for SPPS were carbodiimides.
In addition to dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCCI), N N -diisopropylcarbodiimide
(DIPCDI) is often used. The mechanism of peptide coupling by carbodiimides was
Scheme 13.75. t-Boc Protocol for Solid
Phase Peptide Synthesis
Boc NHCHRCO resin
1. -Boc: CF 3 COOH
2. Wash: DMF
– +
CF 3 COO . NH 3 CHRCO resin
3. Couple: Boc AA OZ + DIPEA a
4. Wash: DMF
Boc AA NHCHRCO resin
a. OZ = active ester; DIPEA = diisopropylethylamine
41 M. Bodanszky and A. Bodanszky, The Practice of Peptide Synthesis, 2nd Edition, Springer Verlag,
Berlin, 1994; V. J. Hruby, and J.-P. Mayer, in Bioorganic Chemistry: Peptides and Proteins, S. Hecht,
ed. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1998, pp. 27–64.
42
R. B. Merrifield, Meth. Enzymol., 289, 3 (1997); R. B. Merrifield, in Peptides: Synthesis, Structure, and
Applications, B. Gutte, ed., Academic Press, San Diego, CA, p. 93; E. Atherton and R. C. Sheppard,
Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis, IRL Press, Oxford, 1989; P. Lloyd-Williams, F. Albericio, and E. Giralt,
Chemical Synthesis of Peptides and Proteins, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1997.