Page 176 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 176
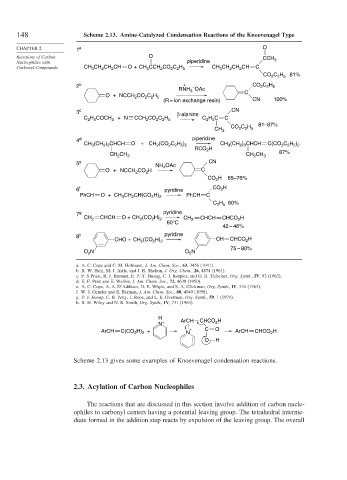
148 Scheme 2.13. Amine-Catalyzed Condensation Reactions of the Knoevenagel Type
CHAPTER 2 1 a O
Reactions of Carbon O CCH
Nucleophiles with piperidine 3
Carbonyl Compounds CH CH CH CH O +CH CCH CO C H CH CH CH CH C
2
3
2
2
2
3
2
2 2 5
3
CO C H 81%
2 2 5
2 b + – CO C H
2 2 5
RNH OAc
3
O + NCCH CO C H C
2 2 5
2
(R = ion exchange resin) CN 100%
3 c β-alanine CN
C H COCH 3 + N CCH 2 CO C H C H C C
2 2 5
2 5
2 5
C H
CH 3 CO 2 2 5 81–87%
4 d piperidine
CH (CH ) CHCH O + CH (CO C H ) CH (CH ) CHCH C(CO C H )
3
2 2 5 2
2 3
2
2 2 5 2
3
2 3
RCO H
2
CH 87%
CH 2 3 CH 2 CH 3
5 e NH OAc CN
4
O + NCCH CO H C
2
2
CO H 65–76%
2
6 f pyridine CO 2 H
PhCH O + CH CH CH(CO H) 2 PhCH C
2
3
2
C 2 H 5 60%
7 g pyridine
CH 2 CHCH O +CH (CO H) 2 CH 2 CHCH CHCO 2 H
2
2
60°C
42 – 46%
8 h pyridine
CHO+CH 2 (CO 2 H) 2 CH CHCO 2 H
75 – 80%
O N O N
2
2
a. A. C. Cope and C. M. Hofmann, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 63, 3456 (1941).
b. R. W. Hein, M. J. Astle, and J. R. Shelton, J. Org. Chem., 26, 4874 (1961).
c. F. S Prout, R. J. Harman, E. P.-Y. Huang, C. J. Korpics, and G. R. Tichelaar, Org. Synth., IV, 93 (1963).
d. E. F. Pratt and E. Werbie, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 72, 4638 (1950).
e. A. C. Cope, A. A. D’Addieco, D. E. Whyte, and S. A. Glickman, Org. Synth., IV, 234 (1963).
f. W. J. Gensler and E. Berman, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 80, 4949 (1958).
g. P. J. Jessup, C. B. Petty, J. Roos, and L. E. Overman, Org. Synth., 59, 1 (1979).
h. R. H. Wiley and N. R. Smith, Org. Synth., IV, 731 (1963).
H
2
N + ArCH CHCO H
ArCH C(CO H) 2 + N + C O ArCH CHCO H
2
2
O H
Scheme 2.13 gives some examples of Knoevenagel condensation reactions.
2.3. Acylation of Carbon Nucleophiles
The reactions that are discussed in this section involve addition of carbon nucle-
ophiles to carbonyl centers having a potential leaving group. The tetrahedral interme-
diate formed in the addition step reacts by expulsion of the leaving group. The overall