Page 358 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 358
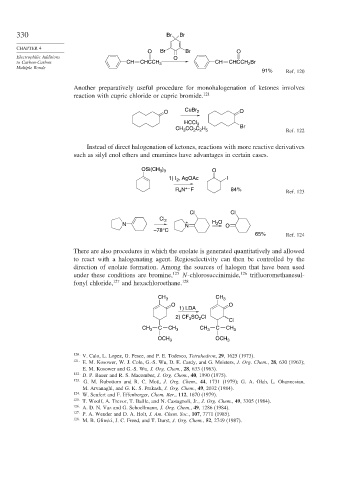
330 Br Br
CHAPTER 4
O Br Br O
Electrophilic Additions O
to Carbon-Carbon CH CHCCH 3 CH CHCCH Br
2
Multiple Bonds
91% Ref. 120
Another preparatively useful procedure for monohalogenation of ketones involves
reaction with cupric chloride or cupric bromide. 121
CuBr
O 2 O
HCCl 3
CH CO C H Br Ref. 122
2 2 5
3
Instead of direct halogenation of ketones, reactions with more reactive derivatives
such as silyl enol ethers and enamines have advantages in certain cases.
OSi(CH ) O
3 3
1) I , AgOAc I
2
N + – F 84%
Ref. 123
R 4
Cl Cl
Cl 2
+
2
N N H O O
–78°C
65% Ref. 124
There are also procedures in which the enolate is generated quantitatively and allowed
to react with a halogenating agent. Regioselectivity can then be controlled by the
direction of enolate formation. Among the sources of halogen that have been used
under these conditions are bromine, 125 N-chlorosuccinimide, 126 trifluoromethanesul-
fonyl chloride, 127 and hexachloroethane. 128
CH 3 CH 3
O O
1) LDA
2) CF SO Cl Cl
2
3
CH 3 C CH 3 CH 3 C CH 3
OCH 3 OCH 3
120
V. Calo, L. Lopez, G. Pesce, and P. E. Todesco, Tetrahedron, 29, 1625 (1973).
121 E. M. Kosower, W. J. Cole, G.-S. Wu, D. E. Cardy, and G. Meisters, J. Org. Chem., 28, 630 (1963);
E. M. Kosower and G.-S. Wu, J. Org. Chem., 28, 633 (1963).
122 D. P. Bauer and R. S. Macomber, J. Org. Chem., 40, 1990 (1975).
123
G. M. Rubottom and R. C. Mott, J. Org. Chem., 44, 1731 (1979); G. A. Olah, L. Ohannesian,
M. Arvanaghi, and G. K. S. Prakash, J. Org. Chem., 49, 2032 (1984).
124 W. Seufert and F. Effenberger, Chem. Ber., 112, 1670 (1979).
125
T. Woolf, A. Trevor, T. Baille, and N. Castagnoli, Jr., J. Org. Chem., 49, 3305 (1984).
126
A. D. N. Vaz and G. Schoellmann, J. Org. Chem., 49, 1286 (1984).
127 P. A. Wender and D. A. Holt, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 107, 7771 (1985).
128
M. B. Glinski, J. C. Freed, and T. Durst, J. Org. Chem., 52, 2749 (1987).