Page 46 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 46
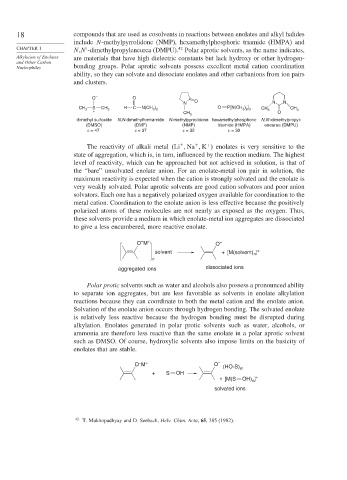
18 compounds that are used as cosolvents in reactions between enolates and alkyl halides
include N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP), hexamethylphosphoric triamide (HMPA) and
42
CHAPTER 1 N,N -dimethylpropyleneurea (DMPU). Polar aprotic solvents, as the name indicates,
Alkylation of Enolates are materials that have high dielectric constants but lack hydroxy or other hydrogen-
and Other Carbon
Nucleophiles bonding groups. Polar aprotic solvents possess excellent metal cation coordination
ability, so they can solvate and dissociate enolates and other carbanions from ion pairs
and clusters.
O – O
N O N N
) ]
CH 3 S CH 3 H C N(CH 3 2 O P[N(CH 3 2 3 CH 3 CH
)
+ O 3
CH 3
dimethyl sulfoxide N,N-dimethylformamide N-methylpyrrolidone hexamethylphosphoric N,N'-dimethylpropyl-
(DMSO) (DMF) (NMP) triamide (HMPA) eneurea (DMPU)
ε = 47 ε = 37 ε = 32 ε = 30
The reactivity of alkali metal Li Na K enolates is very sensitive to the
+
+
+
state of aggregation, which is, in turn, influenced by the reaction medium. The highest
level of reactivity, which can be approached but not achieved in solution, is that of
the “bare” unsolvated enolate anion. For an enolate-metal ion pair in solution, the
maximum reactivity is expected when the cation is strongly solvated and the enolate is
very weakly solvated. Polar aprotic solvents are good cation solvators and poor anion
solvators. Each one has a negatively polarized oxygen available for coordination to the
metal cation. Coordination to the enolate anion is less effective because the positively
polarized atoms of these molecules are not nearly as exposed as the oxygen. Thus,
these solvents provide a medium in which enolate-metal ion aggregates are dissociated
to give a less encumbered, more reactive enolate.
–
O M + O –
solvent + [M(solvent) ] +
n
n
aggregated ions dissociated ions
Polar protic solvents such as water and alcohols also possess a pronounced ability
to separate ion aggregates, but are less favorable as solvents in enolate alkylation
reactions because they can coordinate to both the metal cation and the enolate anion.
Solvation of the enolate anion occurs through hydrogen bonding. The solvated enolate
is relatively less reactive because the hydrogen bonding must be disrupted during
alkylation. Enolates generated in polar protic solvents such as water, alcohols, or
ammonia are therefore less reactive than the same enolate in a polar aprotic solvent
such as DMSO. Of course, hydroxylic solvents also impose limits on the basicity of
enolates that are stable.
–
O M + O –
(HO-S) m
+ S OH
+ [M(S OH) ] +
n
solvated ions
42
T. Mukhopadhyay and D. Seebach, Helv. Chim. Acta, 65, 385 (1982).