Page 780 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 780
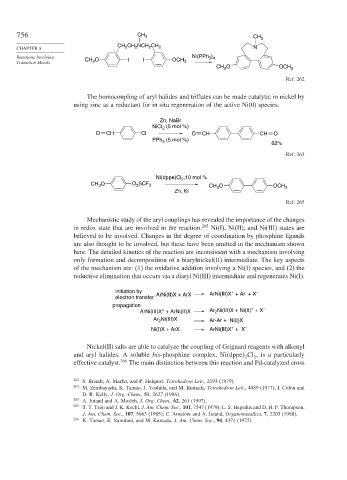
756 CH 3 CH 3
CH NCH CH
CHAPTER 8 CH 2 2 2 2 N
)
Reactions Involving CH O I OCH Ni(PPh 3 4
Transition Metals 3 I 3
CH O OCH 3
3
Ref. 262
The homocoupling of aryl halides and triflates can be made catalytic in nickel by
using zinc as a reductant for in situ regeneration of the active Ni(0) species.
Zn, NaBr
(5 mol %)
NiCl 2
O CH Cl O CH CH O
PPh 3 (5 mol %)
62%
Ref. 263
Ni(dppe)Cl ,10 mol %
2
CH O O SCF 3 CH O OCH 3
3
3
Zn, KI 3
Ref. 265
Mechanistic study of the aryl couplings has revealed the importance of the changes
in redox state that are involved in the reaction. 265 Ni(I), Ni(II), and Ni(III) states are
believed to be involved. Changes in the degree of coordination by phosphine ligands
are also thought to be involved, but these have been omitted in the mechanism shown
here. The detailed kinetics of the reaction are inconsistent with a mechanism involving
only formation and decomposition of a biarylnickel(II) intermediate. The key aspects
of the mechanism are: (1) the oxidative addition involving a Ni(I) species, and (2) the
reductive elimination that occurs via a diaryl Ni(III) intermediate and regenerates Ni(I).
initiation by ArNi(III)X + Ar + X –
.
+
electron transfer ArNi(II)X + ArX
propagation
+
+
ArNi(III)X + ArNi(II)X Ar Ni(III)X + Ni(II) + X –
2
Ar Ni(III)X Ar-Ar + Ni(I)X
2
+
Ni(I)X + ArX ArNi(III)X + X –
Nickel(II) salts are able to catalyze the coupling of Grignard reagents with alkenyl
and aryl halides. A soluble bis-phosphine complex, Ni dppe Cl , is a particularly
2
2
effective catalyst. 266 The main distinction between this reaction and Pd-catalyzed cross
262
S. Brandt, A. Marfat, and P. Helquist, Tetrahedron Lett., 2193 (1979).
263
M. Zembayashi, K. Tamao, J. Yoshida, and M. Kumada, Tetrahedron Lett., 4089 (1977); I. Colon and
D. R. Kelly, J. Org. Chem., 51, 2627 (1986).
265 A. Jutand and A. Mosleh, J. Org. Chem., 62, 261 (1997).
265 T. T. Tsou and J. K. Kochi, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 101, 7547 (1979); L. S. Hegedus and D. H. P. Thompson,
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 107, 5663 (1985); C. Amatore and A. Jutand, Organometallics, 7, 2203 (1988).
266
K. Tamao, K. Sumitani, and M. Kumada, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 94, 4374 (1972).