Page 775 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 775
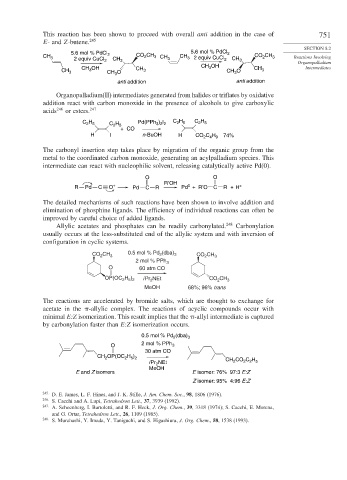
This reaction has been shown to proceed with overall anti addition in the case of 751
E- and Z-butene. 245
SECTION 8.2
5.6 mol % PdCl 5.6 mol % PdCl 2
CH 3 2 equiv CuCl 2 2 CH 3 CO CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 2 equiv CuCl 2 CH 3 CO CH 3 Reactions Involving
2
2
Organopalladium
3
CH 3 CH OH CH O CH 3 CH OH CH O CH 3 Intermediates
3
3
3
anti addition anti addition
Organopalladium(II) intermediates generated from halides or triflates by oxidative
addition react with carbon monoxide in the presence of alcohols to give carboxylic
acids 246 or esters. 247
C H C H Pd(PPh ) I C H C H
2 5
2 5
2 5
3 2 2
2 5
+ CO
H I n-BuOH H CO C H 74%
2 4 9
The carbonyl insertion step takes place by migration of the organic group from the
metal to the coordinated carbon monoxide, generating an acylpalladium species. This
intermediate can react with nucleophilic solvent, releasing catalytically active Pd(0).
O O
R′OH
0
R Pd C O + Pd C R Pd + R′O C R + H +
The detailed mechanisms of such reactions have been shown to involve addition and
elimination of phosphine ligands. The efficiency of individual reactions can often be
improved by careful choice of added ligands.
Allylic acetates and phosphates can be readily carbonylated. 248 Carbonylation
usually occurs at the less-substituted end of the allylic system and with inversion of
configuration in cyclic systems.
CO CH 3 0.5 mol % Pd (dba) 3 CO CH 3
2
2
2
2 mol % PPh 3
O 60 atm CO
OP(OC H ) i Pr NEt CO CH 3
2 5 2
2
2
MeOH 68%; 96% trans
The reactions are accelerated by bromide salts, which are thought to exchange for
acetate in the -allylic complex. The reactions of acyclic compounds occur with
minimal E:Z isomerization. This result implies that the -allyl intermediate is captured
by carbonylation faster than E:Z isomerization occurs.
0.5 mol % Pd (dba) 3
2
O 2 mol % PPh 3
30 atm CO
CH OP(OC H )
2
2 5 2
2 2 5
i Pr NEt CH CO C H
2
2
MeOH
E and Z isomers E isomer: 76% 97:3 E:Z
Z isomer: 95% 4:96 E:Z
245
D. E. James, L. F. Hines, and J. K. Stille, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 98, 1806 (1976).
246
S. Cacchi and A. Lupi, Tetrahedron Lett., 37, 3939 (1992).
247 A. Schoenberg, I. Bartoletti, and R. F. Heck, J. Org. Chem., 39, 3318 (1974); S. Cacchi, E. Morena,
and G. Ortar, Tetrahedron Lett., 26, 1109 (1985).
248
S. Murahashi, Y. Imada, Y. Taniguchi, and S. Higashiura, J. Org. Chem., 58, 1538 (1993).