Page 786 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 786
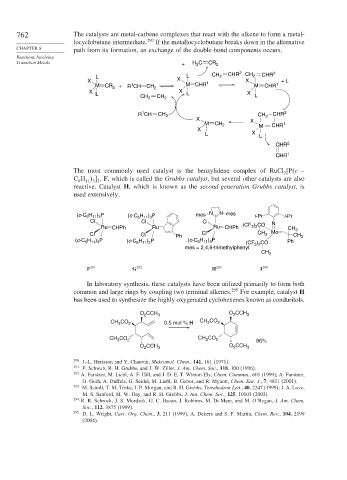
762 The catalysts are metal-carbene complexes that react with the alkene to form a metal-
locyclobutane intermediate. 290 If the metallocyclobutane breaks down in the alternative
CHAPTER 8 path from its formation, an exchange of the double-bond components occurs.
Reactions Involving
Transition Metals + H C CR 2
2
L L CH 2 CHR 2 CH 2 CHR 2
X X 1 X + L
M CR 2 + R CH CH 2 M CHR M CHR 1
1
X X X
L CH 2 CH 2 L L
1
R CH CH 2 CH 2 CHR 2
X X
M CH 2 M CHR 1
X
L X L
CHR 2
CHR 1
The most commonly used catalyst is the benzylidene complex of RuCl P c −
2
C H
, F, which is called the Grubbs catalyst, but several other catalysts are also
11 3 2
6
reactive. Catalyst H, which is known as the second-generation Grubbs catalyst,is
used extensively.
(c-C 6 H 11 ) 3 P (c-C 6 H 11 ) 3 P mes N N mes i-Pr i-Pr
Cl Cl Cl N
Ru CHPh Ru Ru CHPh (CF 3 ) 2 CO CH 3
Cl Cl Ph Cl CH 3 Mo CH 3
(c-C 6 H 11 ) 3 P (c-C 6 H 11 ) 3 P (c-C 6 H 11 ) 3 P (CF 3 ) 2 CO Ph
mes = 2,4,6-trimethylphenyl
CH 3
F 291 G 292 H 293 I 294
In laboratory synthesis, these catalysts have been utilized primarily to form both
common and large rings by coupling two terminal alkenes. 295 For example, catalyst H
has been used to synthesize the highly oxygenated cyclohexenes known as conduritols.
O CCH 3 O CCH 3
2
2
CH CO 2 0.5 mol % H CH CO 2
3
3
CH CO 2 CH CO 2 96%
3
3
O CCH 3 O CCH 3
2
2
290
J.-L. Herisson and Y. Chauvin, Makromol. Chem., 141, 161 (1971).
291 P. Schwab, R. H. Grubbs, and J. W. Ziller, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 118, 100 (1996).
292 A. Furstner, M. Liebl, A. F. Hill, and J. D. E. T. Winton-Ely, Chem. Commun., 601 (1999); A. Furstner,
O. Guth, A. Duffels, G. Seidel, M. Liebl, B. Gabor, and R. Mynott, Chem. Eur. J., 7, 4811 (2001).
293
M. Scholl, T. M. Trnka, J. P. Morgan, and R. H. Grubbs, Tetrahedron Lett., 40, 2247 (1999); J. A. Love,
M. S. Sanford, M. W. Day, and R. H. Grubbs, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 125, 10103 (2003).
294 R. R. Schrock, J. S. Murdzek, G. C. Bazan, J. Robbins, M. Di Mare, and M. O’Regan, J. Am. Chem.
Soc., 112, 3875 (1999).
295
D. L. Wright, Curr. Org. Chem., 3, 211 (1999); A. Deiters and S. F. Martin, Chem. Rev., 104, 2199
(2004).