Page 805 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 805
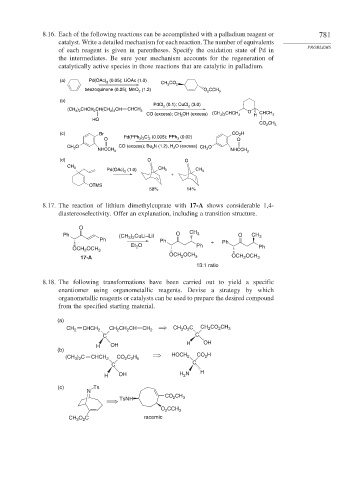
8.16. Each of the following reactions can be accomplished with a palladium reagent or 781
catalyst. Write a detailed mechanism for each reaction. The number of equivalents
PROBLEMS
of each reagent is given in parentheses. Specify the oxidation state of Pd in
the intermediates. Be sure your mechanism accounts for the regeneration of
catalytically active species in those reactions that are catalytic in palladium.
(a) Pd(OAc) 2 (0.05); LiOAc (1.0)
CH 3 CO 2
benzoquinone (0.25), MnO 2 (1.2) O 2 CCH 3
(b)
PdCl 2 (0.1); CuCl 2 (3.0)
(CH 3 ) 2 CHCH 2 CH(CH 2 ) 3 CH CHCH 3
O
CO (excess); CH 3 OH (excess) (CH 3 ) 2 CHCH 2 H CHCH 3
HO
CO 2 CH 3
(c) Br CO 2 H
O Pd(PPh 3 ) 2 Cl 2 (0.005); PPh 3 (0.02) O
CH 3 O CO (excess); Bu 3 N (1.2), H 2 O (excess) CH 3 O
NHCCH 3 NHCCH 3
(d) O O
CH 3
Pd(OAc) 2 (1.0) CH 3 CH 3
+
OTMS
58% 14%
8.17. The reaction of lithium dimethylcuprate with 17-A shows considerable 1,4-
diastereoselectivity. Offer an explanation, including a transition structure.
O
Ph ) CuLi–LiI O CH 3 O CH 3
Ph (CH 3 2 Ph + Ph
Et O Ph
OCH OCH 3 2 Ph
2
OCH OCH OCH OCH
17-A 2 3 2 3
13:1 ratio
8.18. The following transformations have been carried out to yield a specific
enantiomer using organometallic reagents. Devise a strategy by which
organometallic reagents or catalysts can be used to prepare the desired compound
from the specified starting material.
(a)
CH 2 CHCH 2 CH CH CH CH 2 CH 3 O C CH 2 CO CH 3
2
2
2
2
C C
H OH H OH
(b)
2
(CH ) C CHCH 2 CO C H HOCH 2 CO H
3 2
2 2 5
C
C
H OH H 2 N H
(c) Ts
N
CO CH
TsNH 2 3
O CCH 3
2
CH O C racemic
2
3