Page 808 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 808
784 in Section 8.2.3. This chapter emphasizes the use of boranes, silanes, and stannanes
as sources of nucleophilic carbon groups toward a variety of electrophiles, especially
CHAPTER 9 carbonyl compounds.
Carbon-Carbon Allylic derivatives are particularly important in the case of boranes, silanes, and
Bond-Forming Reactions
of Compounds of Boron, stannanes. Allylic boranes effect nucleophilic addition to carbonyl groups via a cyclic
Silicon, and Tin TS that involves the Lewis acid character of the borane. 1,3-Allylic transposition
occurs through the cyclic TS.
B
B O OH
O
R
R R
H R′ R′
R′
Allylic silanes and stannanes react with various electrophiles with demetallation. These
reactions can occur via several related mechanisms. Both types of reagents can deliver
allylic groups to electrophilic centers such as carbonyl and iminium.
X X XH
+
R′ M R′ 3 M
3
H R R R
H
M = Si, Sn X = O, NY
Alkenyl silanes and stannanes have the potential for nucleophilic delivery of vinyl
groups to a variety of electrophiles. Demetallation also occurs in these reactions, so
the net effect is substitution for the silyl or the stannyl group.
X MR 3
MR 3 X R
+
H R H R XH
M = Si, Sn X = O, NY
9.1. Organoboron Compounds
9.1.1. Synthesis of Organoboranes
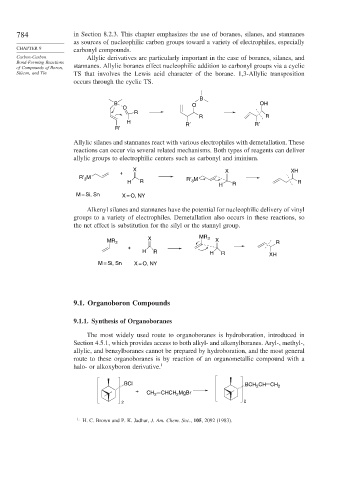
The most widely used route to organoboranes is hydroboration, introduced in
Section 4.5.1, which provides access to both alkyl- and alkenylboranes. Aryl-, methyl-,
allylic, and benzylboranes cannot be prepared by hydroboration, and the most general
route to these organoboranes is by reaction of an organometallic compound with a
halo- or alkoxyboron derivative. 1
BCl BCH CH CH 2
2
+ CH 2 CHCH MgBr
2
2 2
1
H. C. Brown and P. K. Jadhar, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 105, 2092 (1983).