Page 960 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 960
936 CH N
2 2
CH CH CH CH CH CH CH 3 CH (CH ) CH + CH CH(CH ) CH 3
2
2
2 6
2
3
3
3
2 4
2
2
3
hν
CHAPTER 10 38% CH 3 25%
Reactions Involving + CH CH CH(CH ) CH + (CH CH CH ) CHCH
Carbocations, Carbenes, 3 2 2 3 3 3 2 2 2 3
and Radicals as Reactive CH 24% 13%
Intermediates 3
There is some increase in selectivity with functionally substituted carbenes, but it is still
not high enough to prevent formation of mixtures. Phenylchlorocarbene gives a relative
reactivity ratio of 2.1:1:0.09 in insertion reactions with i-propylbenzene, ethylbenzene,
and toluene. 212 For cycloalkanes, tertiary positions are about 15 times more reactive
than secondary positions toward phenylchlorocarbene. 213 Carbethoxycarbene inserts
at tertiary C−H bonds about three times as fast as at primary C−H bonds in simple
alkanes. 214 Owing to low selectivity, intermolecular insertion reactions are seldom
useful in syntheses. Intramolecular insertion reactions are of considerably more value.
Intramolecular insertion reactions usually occur at the C−H bond that is closest to the
carbene and good yields can frequently be achieved. Intramolecular insertion reactions
can provide routes to highly strained structures that would be difficult to obtain in
other ways.
Rhodium carboxylates have been found to be effective catalysts for intramolecular
C−H insertion reactions of -diazo ketones and esters. 215 In flexible systems, five-
membered rings are formed in preference to six-membered ones. Insertion into methine
hydrogen is preferred to a methylene hydrogen. Intramolecular insertion can be compet-
itive with intramolecular addition. Product ratios can to some extent be controlled
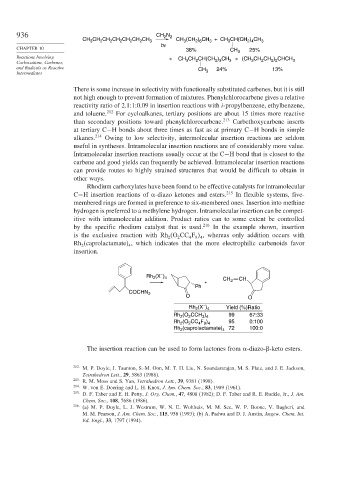
by the specific rhodium catalyst that is used. 216 In the example shown, insertion
is the exclusive reaction with Rh (O CC F , whereas only addition occurs with
2
4 9 4
2
Rh (caprolactamate) , which indicates that the more electrophilic carbenoids favor
4
2
insertion.
–
Rh (X ) 4 CH CH
2
+ 2
Ph
COCHN 2
O O
–
Rh 2 (X ) 4 Yield (%)Ratio
Rh 2 (O 2 CCH 3 ) 4 99 67:33
Rh (O CC F ) 95 0:100
2
4 9 4
2
Rh (caprolactamate) 4 72 100:0
2
The insertion reaction can be used to form lactones from -diazo- -keto esters.
212 M. P. Doyle, J. Taunton, S.-M. Oon, M. T. H. Liu, N. Soundararajan, M. S. Platz, and J. E. Jackson,
Tetrahedron Lett., 29, 5863 (1988).
213
R. M. Moss and S. Yan, Tetrahedron Lett., 39, 9381 (1998).
214 W. von E. Doering and L. H. Knox, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 83, 1989 (1961).
215 D. F. Taber and E. H. Petty, J. Org. Chem., 47, 4808 (1982); D. F. Taber and R. E. Ruckle, Jr., J. Am.
Chem. Soc., 108, 7686 (1986).
216
(a) M. P. Doyle, L. J. Westrum, W. N. E. Wolthuis, M. M. See, W. P. Boone, V. Bagheri, and
M. M. Pearson, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 115, 958 (1993); (b) A. Padwa and D. J. Austin, Angew. Chem. Int.
Ed. Engl., 33, 1797 (1994).