Page 961 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 961
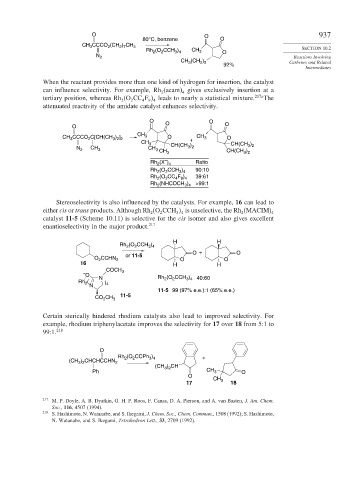
O O 937
80°C, benzene O
CH CCCO (CH ) CH 3
3
2 7
2
Rh (O CCH ) CH 3 O SECTION 10.2
3 4
2
2
N 2 Reactions Involving
CH 3 (CH ) Carbenes and Related
2 5
92%
Intermediates
When the reactant provides more than one kind of hydrogen for insertion, the catalyst
can influence selectivity. For example, Rh (acam) gives exclusively insertion at a
4
2
tertiary position, whereas Rh (O CC F leads to nearly a statistical mixture. 217a The
2
2
4 9 4
attenuated reactivity of the amidate catalyst enhances selectivity.
O O
O O O
CH
CH CCCO C[CH(CH ) ] 3 O CH 3 O
2
3
3 2 2
CH 3 CH(CH ) + CH(CH )
N 2 CH 3 CH 3 3 2 3 2
CH 3 CH(CH 3 ) 2
–
Rh (X ) 4 Ratio
2
Rh (O CCH ) 90:10
2
2
3 4
Rh (O CC F ) 39:61
4 9 4
2
2
3 4 >99:1
Rh (NHCOCH )
2
Stereoselectivity is also influenced by the catalysts. For example, 16 can lead to
either cis or trans products. Although Rh (O CCH is unselective, the Rh (MACIM) 4
3 4
2
2
2
catalyst 11-5 (Scheme 10.11) is selective for the cis isomer and also gives excellent
enantioselectivity in the major product. 217
H H
Rh (O CCH )
2
2
3 4
O + O
or 11-5
O CCHN 2 O O
2
16 H H
COCH 3
–
O Rh (O CCH )
Rh ( N ) 4 2 2 3 4 40:60
2
N
11-5 99 (97% e.e.):1 (65% e.e.)
CO CH 3 11-5
2
Certain sterically hindered rhodium catalysts also lead to improved selectivity. For
example, rhodium triphenylacetate improves the selectivity for 17 over 18 from 5:1 to
99:1. 218
O
Rh (O CCPh ) +
3 4
2
2
(CH ) CHCHCCHN 2
3 2
(CH ) 2 CH
3
Ph CH 3 O
O CH
17 3 18
217 M. P. Doyle, A. B. Dyatkin, G. H. P. Roos, F. Canas, D. A. Pierson, and A. van Basten, J. Am. Chem.
Soc., 116, 4507 (1994).
218
S. Hashimoto, N. Watanabe, and S. Ikegami, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1508 (1992); S. Hashimoto,
N. Watanabe, and S. Ikegami, Tetrahedron Lett., 33, 2709 (1992).