Page 61 - Advanced thermodynamics for engineers
P. 61
3.2 AIR-STANDARD CYCLES 45
180
160
140 constant
volume
combustion
Pressure, p / (bar) 100 compression
120
Isentropic
80
and
60
40 expansion
20
0
0 0.0005 0.0010 0.0015 0.0020 0.0025 0.0030
3
Volume, V / (m )
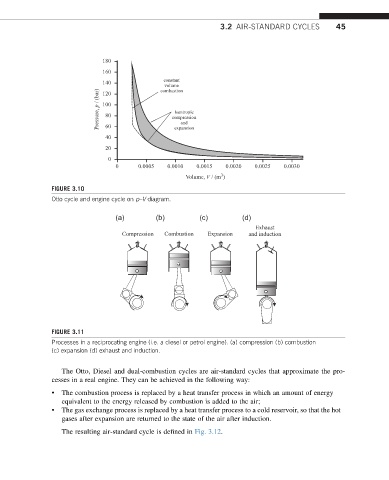
FIGURE 3.10
Otto cycle and engine cycle on p–V diagram.
(a) (b) (c) (d)
Exhaust
Compression Combustion Expansion and induction
FIGURE 3.11
Processes in a reciprocating engine (i.e. a diesel or petrol engine). (a) compression (b) combustion
(c) expansion (d) exhaust and induction.
The Otto, Diesel and dual-combustion cycles are air-standard cycles that approximate the pro-
cesses in a real engine. They can be achieved in the following way:
• The combustion process is replaced by a heat transfer process in which an amount of energy
equivalent to the energy released by combustion is added to the air;
• The gas exchange process is replaced by a heat transfer process to a cold reservoir, so that the hot
gases after expansion are returned to the state of the air after induction.
The resulting air-standard cycle is defined in Fig. 3.12.