Page 399 - Advanced Mine Ventilation
P. 399
368 Advanced Mine Ventilation
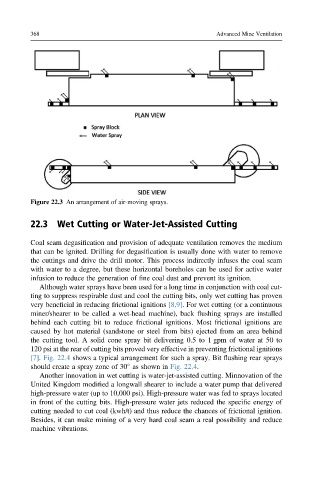
Figure 22.3 An arrangement of air-moving sprays.
22.3 Wet Cutting or Water-Jet-Assisted Cutting
Coal seam degasification and provision of adequate ventilation removes the medium
that can be ignited. Drilling for degasification is usually done with water to remove
the cuttings and drive the drill motor. This process indirectly infuses the coal seam
with water to a degree, but these horizontal boreholes can be used for active water
infusion to reduce the generation of fine coal dust and prevent its ignition.
Although water sprays have been used for a long time in conjunction with coal cut-
ting to suppress respirable dust and cool the cutting bits, only wet cutting has proven
very beneficial in reducing frictional ignitions [8,9]. For wet cutting (or a continuous
miner/shearer to be called a wet-head machine), back flushing sprays are installed
behind each cutting bit to reduce frictional ignitions. Most frictional ignitions are
caused by hot material (sandstone or steel from bits) ejected from an area behind
the cutting tool. A solid cone spray bit delivering 0.5 to 1 gpm of water at 50 to
120 psi at the rear of cutting bits proved very effective in preventing frictional ignitions
[7]. Fig. 22.4 shows a typical arrangement for such a spray. Bit flushing rear sprays
should create a spray zone of 30 as shown in Fig. 22.4.
Another innovation in wet cutting is water-jet-assisted cutting. Minnovation of the
United Kingdom modified a longwall shearer to include a water pump that delivered
high-pressure water (up to 10,000 psi). High-pressure water was fed to sprays located
in front of the cutting bits. High-pressure water jets reduced the specific energy of
cutting needed to cut coal (kwh/t) and thus reduce the chances of frictional ignition.
Besides, it can make mining of a very hard coal seam a real possibility and reduce
machine vibrations.