Page 172 - Advances in bioenergy (2016)
P. 172
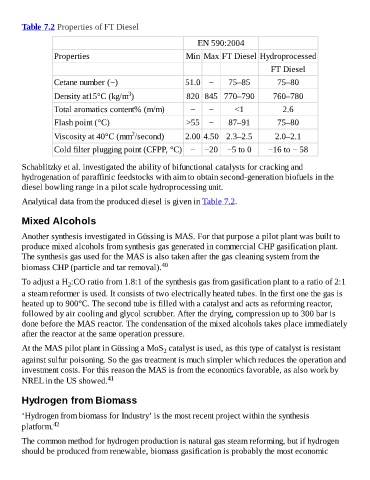
Table 7.2 Properties of FT Diesel
EN 590:2004
Properties Min Max FT Diesel Hydroprocessed
FT Diesel
Cetane number (−) 51.0 − 75–85 75–80
3
Density at15°C (kg/m ) 820 845 770–790 760–780
Total aromatics content% (m/m) − − <1 2.6
Flash point (°C) >55 − 87–91 75–80
2
Viscosity at 40°C (mm /second) 2.00 4.50 2.3–2.5 2.0–2.1
Cold filter plugging point (CFPP, °C) − −20 −5 to 0 −16 to − 58
Schablitzky et al. investigated the ability of bifunctional catalysts for cracking and
hydrogenation of paraffinic feedstocks with aim to obtain second-generation biofuels in the
diesel bowling range in a pilot scale hydroprocessing unit.
Analytical data from the produced diesel is given in Table 7.2.
Mixed Alcohols
Another synthesis investigated in Güssing is MAS. For that purpose a pilot plant was built to
produce mixed alcohols from synthesis gas generated in commercial CHP gasification plant.
The synthesis gas used for the MAS is also taken after the gas cleaning system from the
biomass CHP (particle and tar removal). 40
To adjust a H :CO ratio from 1.8:1 of the synthesis gas from gasification plant to a ratio of 2:1
2
a steam reformer is used. It consists of two electrically heated tubes. In the first one the gas is
heated up to 900°C. The second tube is filled with a catalyst and acts as reforming reactor,
followed by air cooling and glycol scrubber. After the drying, compression up to 300 bar is
done before the MAS reactor. The condensation of the mixed alcohols takes place immediately
after the reactor at the same operation pressure.
At the MAS pilot plant in Güssing a MoS catalyst is used, as this type of catalyst is resistant
2
against sulfur poisoning. So the gas treatment is much simpler which reduces the operation and
investment costs. For this reason the MAS is from the economics favorable, as also work by
NREL in the US showed. 41
Hydrogen from Biomass
‘Hydrogen from biomass for Industry’ is the most recent project within the synthesis
platform. 42
The common method for hydrogen production is natural gas steam reforming, but if hydrogen
should be produced from renewable, biomass gasification is probably the most economic