Page 195 - Advances in bioenergy (2016)
P. 195
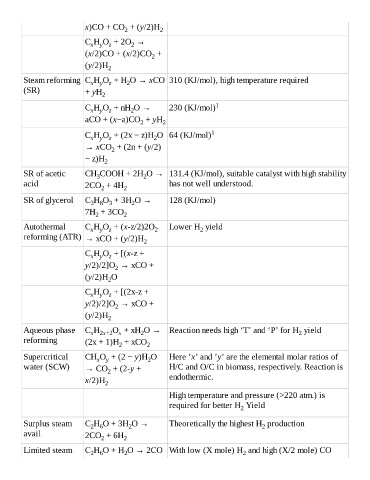
x)CO + CO + (y/2)H 2
2
C H O + 2O →
x y z 2
(x/2)CO + (x/2)CO +
2
(y/2)H 2
Steam reforming C H O + H O → xCO 310 (KJ/mol), high temperature required
2
x y z
(SR) + yH 2
C H O + nH O → 230 (KJ/mol) 1
2
x y z
aCO + (x−a)CO + yH 2
2
C H O + (2x − z)H O 64 (KJ/mol) 1
x y z
2
→ xCO + (2n + (y/2)
2
− z)H
2
SR of acetic CH COOH + 2H O → 131.4 (KJ/mol), suitable catalyst with high stability
2
3
acid 2CO + 4H 2 has not well understood.
2
SR of glycerol C H O + 3H O → 128 (KJ/mol)
3 8 3
2
7H + 3CO 2
2
Autothermal C H O + (x-z/2)2O 2 Lower H yield
x y z
2
reforming (ATR) → xCO + (y/2)H 2
C H O + [(x-z +
x y z
y/2)/2]O → xCO +
2
(y/2)H O
2
C H O + [(2x-z +
x y z
y/2)/2]O → xCO +
2
(y/2)H 2
Aqueous phase C H O + xH O → Reaction needs high ‘T’ and ‘P’ for H yield
x 2x+2 x
2
2
reforming (2x + 1)H + xCO 2
2
Supercritical CH O + (2 − y)H O Here ’x’ and ’y’ are the elemental molar ratios of
x y
2
water (SCW) → CO + (2-y + H/C and O/C in biomass, respectively. Reaction is
2
x/2)H 2 endothermic.
High temperature and pressure (>220 atm.) is
required for better H Yield
2
Surplus steam C H O + 3H O → Theoretically the highest H production
2 6 2 2
avail 2CO + 6H 2
2
Limited steam C H O + H O → 2CO With low (X mole) H and high (X/2 mole) CO
2 6
2
2