Page 196 - Advances in bioenergy (2016)
P. 196
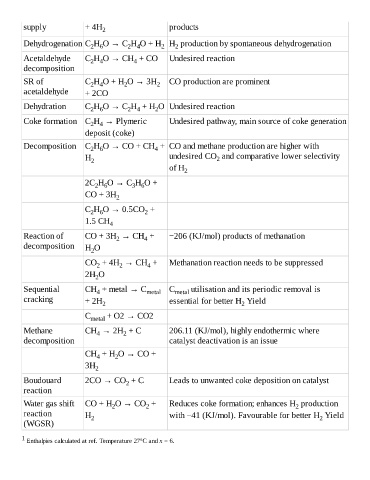
supply + 4H 2 products
Dehydrogenation C H O → C H O + H H production by spontaneous dehydrogenation
2
2 4
2 6
2
Acetaldehyde C H O → CH + CO Undesired reaction
2 4
4
decomposition
SR of C H O + H O → 3H 2 CO production are prominent
2
2 4
acetaldehyde + 2CO
Dehydration C H O → C H + H O Undesired reaction
2
2 6
2 4
Coke formation C H → Plymeric Undesired pathway, main source of coke generation
2 4
deposit (coke)
Decomposition C H O → CO + CH + CO and methane production are higher with
2 6
4
H 2 undesired CO and comparative lower selectivity
2
of H 2
2C H O → C H O +
3 6
2 6
CO + 3H
2
C H O → 0.5CO +
2
2 6
1.5 CH 4
Reaction of CO + 3H → CH + −206 (KJ/mol) products of methanation
2
4
decomposition H O
2
CO + 4H → CH + Methanation reaction needs to be suppressed
4
2
2
2H O
2
Sequential CH + metal → C metal C metal utilisation and its periodic removal is
4
cracking + 2H 2 essential for better H Yield
2
C metal + O2 → CO2
Methane CH → 2H + C 206.11 (KJ/mol), highly endothermic where
4
2
decomposition catalyst deactivation is an issue
CH + H O → CO +
2
4
3H 2
Boudouard 2CO → CO + C Leads to unwanted coke deposition on catalyst
2
reaction
Water gas shift CO + H O → CO + Reduces coke formation; enhances H production
2
2
2
reaction H 2 with −41 (KJ/mol). Favourable for better H Yield
2
(WGSR)
1
Enthalpies calculated at ref. Temperature 27°C and x = 6.