Page 186 - Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment
P. 186
150 Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment
5.14 Comparison of calorific value for the different
pyrolysis oil
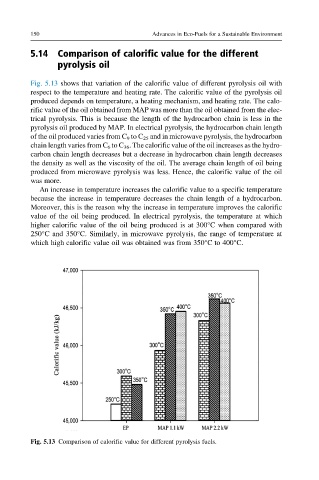
Fig. 5.13 shows that variation of the calorific value of different pyrolysis oil with
respect to the temperature and heating rate. The calorific value of the pyrolysis oil
produced depends on temperature, a heating mechanism, and heating rate. The calo-
rific value of the oil obtained from MAP was more than the oil obtained from the elec-
trical pyrolysis. This is because the length of the hydrocarbon chain is less in the
pyrolysis oil produced by MAP. In electrical pyrolysis, the hydrocarbon chain length
of the oil produced varies from C 9 to C 25 and in microwave pyrolysis, the hydrocarbon
chain length varies from C 6 to C 36 . The calorific value of the oil increases as the hydro-
carbon chain length decreases but a decrease in hydrocarbon chain length decreases
the density as well as the viscosity of the oil. The average chain length of oil being
produced from microwave pyrolysis was less. Hence, the calorific value of the oil
was more.
An increase in temperature increases the calorific value to a specific temperature
because the increase in temperature decreases the chain length of a hydrocarbon.
Moreover, this is the reason why the increase in temperature improves the calorific
value of the oil being produced. In electrical pyrolysis, the temperature at which
higher calorific value of the oil being produced is at 300°C when compared with
250°C and 350°C. Similarly, in microwave pyrolysis, the range of temperature at
which high calorific value oil was obtained was from 350°C to 400°C.
Fig. 5.13 Comparison of calorific value for different pyrolysis fuels.