Page 187 - Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment
P. 187
Microwave-assisted fast pyrolysis of hazardous waste engine oil into green fuels 151
The calorific value of the oil was improved with an increase in heating rate. The
calorific value of the pyrolysis oil was more for a 2.2kW heating rate when compared
with a 1.1kW heating rate. This was due to the increased cracking of hydrocarbon
chain into smaller molecules. The calorific value decreases for microwave pyrolysis
at 2.2kW heating and above 350°C were because of the chances of decreased H/C
ratio due to the formation of cycloalkanes and alkenes.
5.15 Comparison of kinematic viscosity of the different
pyrolysis oils
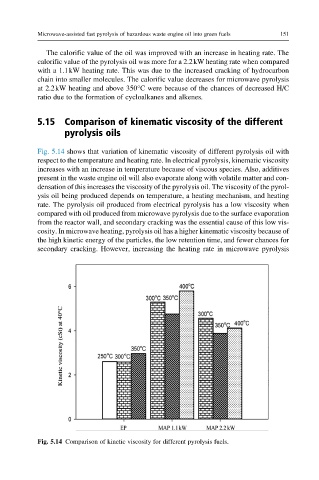
Fig. 5.14 shows that variation of kinematic viscosity of different pyrolysis oil with
respect to the temperature and heating rate. In electrical pyrolysis, kinematic viscosity
increases with an increase in temperature because of viscous species. Also, additives
present in the waste engine oil will also evaporate along with volatile matter and con-
densation of this increases the viscosity of the pyrolysis oil. The viscosity of the pyrol-
ysis oil being produced depends on temperature, a heating mechanism, and heating
rate. The pyrolysis oil produced from electrical pyrolysis has a low viscosity when
compared with oil produced from microwave pyrolysis due to the surface evaporation
from the reactor wall, and secondary cracking was the essential cause of this low vis-
cosity. In microwave heating, pyrolysis oil has a higher kinematic viscosity because of
the high kinetic energy of the particles, the low retention time, and fewer chances for
secondary cracking. However, increasing the heating rate in microwave pyrolysis
Fig. 5.14 Comparison of kinetic viscosity for different pyrolysis fuels.