Page 239 - Advances in Forensic Applications of Mass Spectrometry - Jehuda Yinon
P. 239
1522_book.fm Page 212 Thursday, November 13, 2003 9:58 AM
Chromatogram Plots
File: I:\data 0999\T5704ms 2.ms
Sample: 10.0 M IN SAMPLING TIME, 5M IN DESORB, GB 16/9/99 10.37 AM
Sample Notes: RN 0391-01, 990-0817-F#1, STAIR TREADS -GC/MS/MS-GB
Operator: D.SUTHERLAND Scan Range: 1-1034 Time Range: 0.02-15.00 min.
Specl 1 7.099m In.scan: 343 chan: 1 Ion: NA RIC: 12512
BP 131 (3894-100%) 15704 ms2.ms 131
100%
75%
119
50%
105
25% 91 147
57 75 84 165 181 194 202
0%
Specl 2 7.243m In.scan: 350 chan: 1 Ion: NA RIC: 11158
100% BP 131 (2642-100%) 15704 ms2.ms 115 131
75%
50% 105
25% 91 145
59 161 170 179 189 207
0%
D Tll Specl 1 - Specl 2 7.099m In.scan: 343 chan: 1 Ion: NA RIC: 12512
100% Normalized 7.243m In.scan: 350 chan: 1 Ion: NA RIC: 11158
50%
0%
-50%
-100%
50 75 100 125 150 175 200 m/z
kCounts 15704ms 42.ms: Ions: 131 all
3
2
1
Counts 15704m 42.ms Ions: 146 all
700
600
500
400
300
200
100
6 7 8 9 minutes
2 3
289 338 387 433 scans
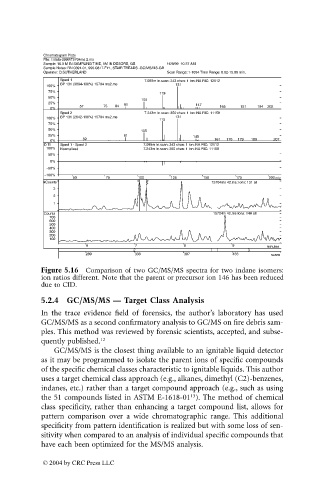
Figure 5.16 Comparison of two GC/MS/MS spectra for two indane isomers:
ion ratios different. Note that the parent or precursor ion 146 has been reduced
due to CID.
5.2.4 GC/MS/MS — Target Class Analysis
In the trace evidence field of forensics, the author’s laboratory has used
GC/MS/MS as a second confirmatory analysis to GC/MS on fire debris sam-
ples. This method was reviewed by forensic scientists, accepted, and subse-
quently published. 12
GC/MS/MS is the closest thing available to an ignitable liquid detector
as it may be programmed to isolate the parent ions of specific compounds
of the specific chemical classes characteristic to ignitable liquids. This author
uses a target chemical class approach (e.g., alkanes, dimethyl (C2)-benzenes,
indanes, etc.) rather than a target compound approach (e.g., such as using
the 51 compounds listed in ASTM E-1618-01 ). The method of chemical
13
class specificity, rather than enhancing a target compound list, allows for
pattern comparison over a wide chromatographic range. This additional
specificity from pattern identification is realized but with some loss of sen-
sitivity when compared to an analysis of individual specific compounds that
have each been optimized for the MS/MS analysis.
© 2004 by CRC Press LLC