Page 293 - Advances in Renewable Energies and Power Technologies
P. 293
266 CHAPTER 8 Hybrid PV/Batteries Bank/Diesel Generator
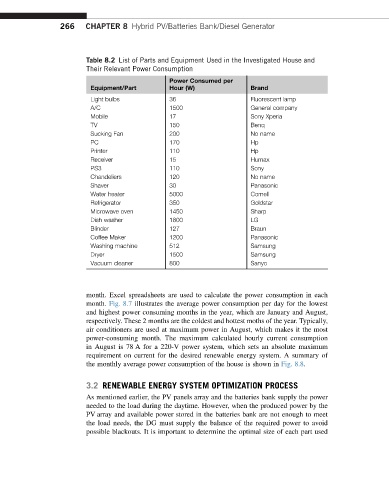
Table 8.2 List of Parts and Equipment Used in the Investigated House and
Their Relevant Power Consumption
Power Consumed per
Equipment/Part Hour (W) Brand
Light bulbs 36 Fluorescent lamp
A/C 1500 General company
Mobile 17 Sony Xperia
TV 150 Benq
Sucking Fan 200 No name
PC 170 Hp
Printer 110 Hp
Receiver 15 Humax
PS3 110 Sony
Chandeliers 120 No name
Shaver 30 Panasonic
Water heater 5000 Cornell
Refrigerator 350 Goldstar
Microwave oven 1450 Sharp
Dish washer 1800 LG
Blinder 127 Braun
Coffee Maker 1200 Panasonic
Washing machine 512 Samsung
Dryer 1500 Samsung
Vacuum cleaner 800 Sanyo
month. Excel spreadsheets are used to calculate the power consumption in each
month. Fig. 8.7 illustrates the average power consumption per day for the lowest
and highest power consuming months in the year, which are January and August,
respectively. These 2 months are the coldest and hottest moths of the year. Typically,
air conditioners are used at maximum power in August, which makes it the most
power-consuming month. The maximum calculated hourly current consumption
in August is 78 A for a 220-V power system, which sets an absolute maximum
requirement on current for the desired renewable energy system. A summary of
the monthly average power consumption of the house is shown in Fig. 8.8.
3.2 RENEWABLE ENERGY SYSTEM OPTIMIZATION PROCESS
As mentioned earlier, the PV panels array and the batteries bank supply the power
needed to the load during the daytime. However, when the produced power by the
PV array and available power stored in the batteries bank are not enough to meet
the load needs, the DG must supply the balance of the required power to avoid
possible blackouts. It is important to determine the optimal size of each part used