Page 305 - Advances in Renewable Energies and Power Technologies
P. 305
278 CHAPTER 8 Hybrid PV/Batteries Bank/Diesel Generator
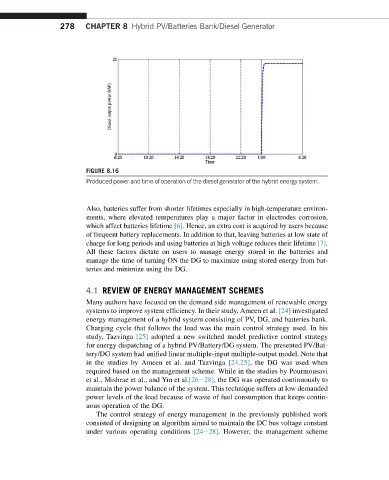
FIGURE 8.16
Produced power and time of operation of the diesel generator of the hybrid energy system.
Also, batteries suffer from shorter lifetimes especially in high-temperature environ-
ments, where elevated temperatures play a major factor in electrodes corrosion,
which affect batteries lifetime [6]. Hence, an extra cost is acquired by users because
of frequent battery replacements. In addition to that, leaving batteries at low state of
charge for long periods and using batteries at high voltage reduces their lifetime [7].
All these factors dictate on users to manage energy stored in the batteries and
manage the time of turning ON the DG to maximize using stored energy from bat-
teries and minimize using the DG.
4.1 REVIEW OF ENERGY MANAGEMENT SCHEMES
Many authors have focused on the demand side management of renewable energy
systems to improve system efficiency. In their study, Ameen et al. [24] investigated
energy management of a hybrid system consisting of PV, DG, and batteries bank.
Charging cycle that follows the load was the main control strategy used. In his
study, Tazvinga [25] adopted a new switched model predictive control strategy
for energy dispatching of a hybrid PV/Battery/DG system. The presented PV/Bat-
tery/DG system had unified linear multiple-input multiple-output model. Note that
in the studies by Ameen et al. and Tazvinga [24,25], the DG was used when
required based on the management scheme. While in the studies by Pourmousavi
et al., Mishraeetal.,and Yinetal.[26e28], the DG was operated continuously to
maintain the power balance of the system. This technique suffers at low demanded
power levels of the load because of waste of fuel consumption that keeps contin-
uous operation of the DG.
The control strategy of energy management in the previously published work
consisted of designing an algorithm aimed to maintain the DC bus voltage constant
under various operating conditions [24e28]. However, the management scheme