Page 348 - Advances in Renewable Energies and Power Technologies
P. 348
4. Modeling and Simulation of Photovoltaic Irrigation System 321
Elevational Angle
Azimuthal
South(oγ)
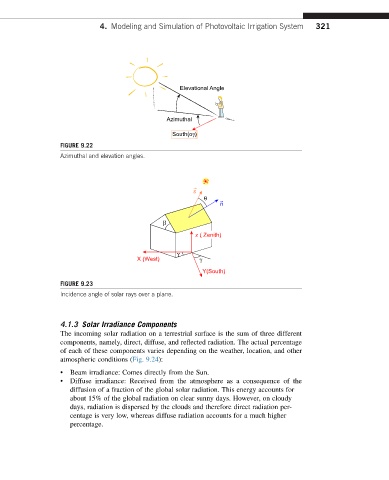
FIGURE 9.22
Azimuthal and elevation angles.
s
θ
n
β
z ( Zenith)
γ
X (West) γ
Y(South)
FIGURE 9.23
Incidence angle of solar rays over a plane.
4.1.3 Solar Irradiance Components
The incoming solar radiation on a terrestrial surface is the sum of three different
components, namely, direct, diffuse, and reflected radiation. The actual percentage
of each of these components varies depending on the weather, location, and other
atmospheric conditions (Fig. 9.24):
• Beam irradiance: Comes directly from the Sun.
• Diffuse irradiance: Received from the atmosphere as a consequence of the
diffusion of a fraction of the global solar radiation. This energy accounts for
about 15% of the global radiation on clear sunny days. However, on cloudy
days, radiation is dispersed by the clouds and therefore direct radiation per-
centage is very low, whereas diffuse radiation accounts for a much higher
percentage.