Page 346 - Advances in Renewable Energies and Power Technologies
P. 346
4. Modeling and Simulation of Photovoltaic Irrigation System 319
14
12
4 pumps on
3 pumps
10
2 pumps
8
Q (L s -1 ) 6 1 pump on
All pumps off
4
1 sector
2 sectors
1 pump on 4 sectors
2 3 sectors
Variable sectors
0
0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500
Incoming power (W)
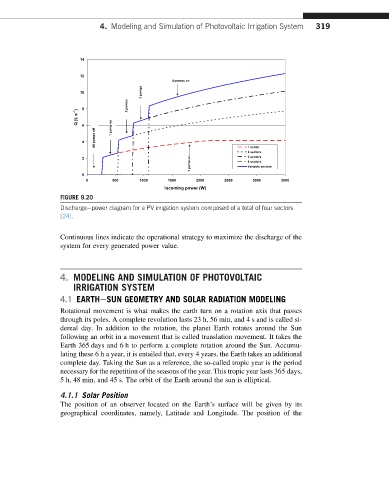
FIGURE 9.20
Dischargeepower diagram for a PV irrigation system composed of a total of four sectors
[24].
Continuous lines indicate the operational strategy to maximize the discharge of the
system for every generated power value.
4. MODELING AND SIMULATION OF PHOTOVOLTAIC
IRRIGATION SYSTEM
4.1 EARTHeSUN GEOMETRY AND SOLAR RADIATION MODELING
Rotational movement is what makes the earth turn on a rotation axis that passes
through its poles. A complete revolution lasts 23 h, 56 min, and 4 s and is called si-
dereal day. In addition to the rotation, the planet Earth rotates around the Sun
following an orbit in a movement that is called translation movement. It takes the
Earth 365 days and 6 h to perform a complete rotation around the Sun. Accumu-
lating these 6 h a year, it is entailed that, every 4 years, the Earth takes an additional
complete day. Taking the Sun as a reference, the so-called tropic year is the period
necessary for the repetition of the seasons of the year. This tropic year lasts 365 days,
5 h, 48 min, and 45 s. The orbit of the Earth around the sun is elliptical.
4.1.1 Solar Position
The position of an observer located on the Earth’s surface will be given by its
geographical coordinates, namely, Latitude and Longitude. The position of the