Page 43 - Air Pollution Control Engineering
P. 43
01_chap_wang.qxd 05/05/2004 11:45 am Page 23
Air Quality and Pollution Control 23
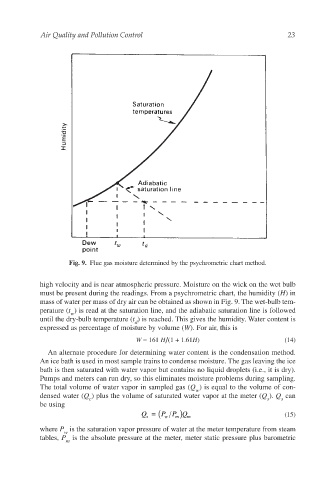
Fig. 9. Flue gas moisture determined by the psychrometric chart method.
high velocity and is near atmospheric pressure. Moisture on the wick on the wet bulb
must be present during the readings. From a psychrometric chart, the humidity (H) in
mass of water per mass of dry air can be obtained as shown in Fig. 9. The wet-bulb tem-
perature (t ) is read at the saturation line, and the adiabatic saturation line is followed
w
until the dry-bulb temperature (t ) is reached. This gives the humidity. Water content is
d
expressed as percentage of moisture by volume (W). For air, this is
W = 161 H/ (1 + 1.61H) (14)
An alternate procedure for determining water content is the condensation method.
An ice bath is used in most sample trains to condense moisture. The gas leaving the ice
bath is then saturated with water vapor but contains no liquid droplets (i.e., it is dry).
Pumps and meters can run dry, so this eliminates moisture problems during sampling.
The total volume of water vapor in sampled gas (Q ) is equal to the volume of con-
w
densed water (Q ) plus the volume of saturated water vapor at the meter (Q ). Q can
c s s
be using
P P Q )
Q = ( w (15)
s m m
where P is the saturation vapor pressure of water at the meter temperature from steam
w
tables, P is the absolute pressure at the meter, meter static pressure plus barometric
m