Page 106 - Air and gas Drilling Field Guide 3rd Edition
P. 106
5.3 Continuous Flow (Dynamic) Compressors 97
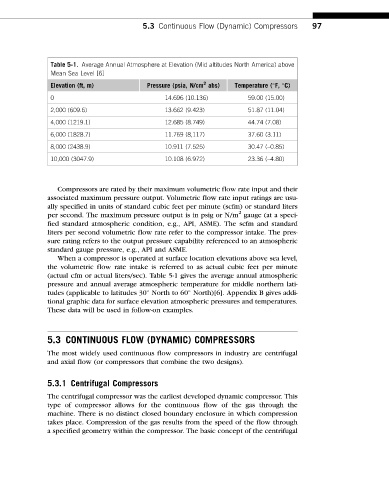
Table 5-1. Average Annual Atmosphere at Elevation (Mid altitudes North America) above
Mean Sea Level [6]
2
Elevation (ft, m) Pressure (psia, N/cm abs) Temperature ( F, C)
0 14.696 (10.136) 59.00 (15.00)
2,000 (609.6) 13.662 (9.423) 51.87 (11.04)
4,000 (1219.1) 12.685 (8.749) 44.74 (7.08)
6,000 (1828.7) 11.769 (8,117) 37.60 (3.11)
8,000 (2438.9) 10.911 (7.525) 30.47 (–0.85)
10,000 (3047.9) 10.108 (6.972) 23.36 (–4.80)
Compressors are rated by their maximum volumetric flow rate input and their
associated maximum pressure output. Volumetric flow rate input ratings are usu-
ally specified in units of standard cubic feet per minute (scfm) or standard liters
2
per second. The maximum pressure output is in psig or N/m gauge (at a speci-
fied standard atmospheric condition, e.g., API, ASME). The scfm and standard
liters per second volumetric flow rate refer to the compressor intake. The pres-
sure rating refers to the output pressure capability referenced to an atmospheric
standard gauge pressure, e.g., API and ASME.
When a compressor is operated at surface location elevations above sea level,
the volumetric flow rate intake is referred to as actual cubic feet per minute
(actual cfm or actual liters/sec). Table 5-1 gives the average annual atmospheric
pressure and annual average atmospheric temperature for middle northern lati-
tudes (applicable to latitudes 30 North to 60 North)[6]. Appendix B gives addi-
tional graphic data for surface elevation atmospheric pressures and temperatures.
These data will be used in follow-on examples.
5.3 CONTINUOUS FLOW (DYNAMIC) COMPRESSORS
The most widely used continuous flow compressors in industry are centrifugal
and axial flow (or compressors that combine the two designs).
5.3.1 Centrifugal Compressors
The centrifugal compressor was the earliest developed dynamic compressor. This
type of compressor allows for the continuous flow of the gas through the
machine. There is no distinct closed boundary enclosure in which compression
takes place. Compression of the gas results from the speed of the flow through
a specified geometry within the compressor. The basic concept of the centrifugal