Page 333 -
P. 333
Chapter 8 ■ Classification 307
(a) (b)
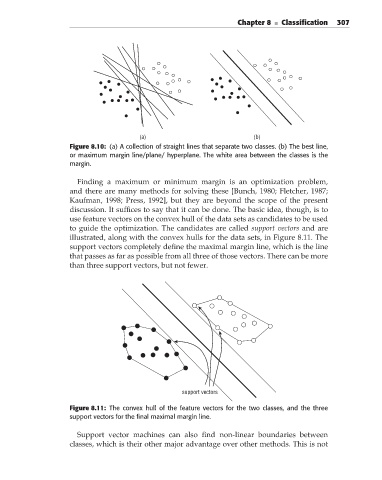
Figure 8.10: (a) A collection of straight lines that separate two classes. (b) The best line,
or maximum margin line/plane/ hyperplane. The white area between the classes is the
margin.
Finding a maximum or minimum margin is an optimization problem,
and there are many methods for solving these [Bunch, 1980; Fletcher, 1987;
Kaufman, 1998; Press, 1992], but they are beyond the scope of the present
discussion. It suffices to say that it can be done. The basic idea, though, is to
use feature vectors on the convex hull of the data sets as candidates to be used
to guide the optimization. The candidates are called support vectors and are
illustrated, along with the convex hulls for the data sets, in Figure 8.11. The
support vectors completely define the maximal margin line, which is the line
that passes as far as possible from all three of those vectors. There can be more
than three support vectors, but not fewer.
support vectors
Figure 8.11: The convex hull of the feature vectors for the two classes, and the three
support vectors for the final maximal margin line.
Support vector machines can also find non-linear boundaries between
classes, which is their other major advantage over other methods. This is not