Page 109 - An Introduction to Microelectromechanical Systems Engineering
P. 109
88 MEM Structures and Systems in Industrial and Automotive Applications
surface where through-holes are desired. Metal is then electroplated everywhere in
the mandrel that is not protected by the photoresist. Finally, the plated metal-foil
structure is peeled off of the mandrel and the resist is stripped. A later section in this
chapter describes the inkjet head in greater detail.
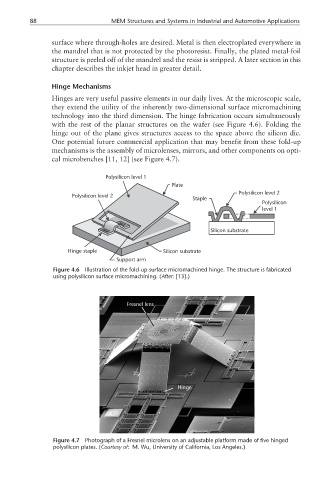
Hinge Mechanisms
Hinges are very useful passive elements in our daily lives. At the microscopic scale,
they extend the utility of the inherently two-dimensional surface micromachining
technology into the third dimension. The hinge fabrication occurs simultaneously
with the rest of the planar structures on the wafer (see Figure 4.6). Folding the
hinge out of the plane gives structures access to the space above the silicon die.
One potential future commercial application that may benefit from these fold-up
mechanisms is the assembly of microlenses, mirrors, and other components on opti-
cal microbenches [11, 12] (see Figure 4.7).
Polysilicon level 1
Plate
Polysilicon level 2
Polysilicon level 2
Staple
Polysilicon
level 1
Silicon substrate
Hinge staple Silicon substrate
Support arm
Figure 4.6 Illustration of the fold-up surface micromachined hinge. The structure is fabricated
using polysilicon surface micromachining. (After: [13].)
Fresnel lens
Hinge
Figure 4.7 Photograph of a Fresnel microlens on an adjustable platform made of five hinged
polysilicon plates. (Courtesy of: M. Wu, University of California, Los Angeles.)