Page 37 - Analytical Electrochemistry 2d Ed - Jospeh Wang
P. 37
22 FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS
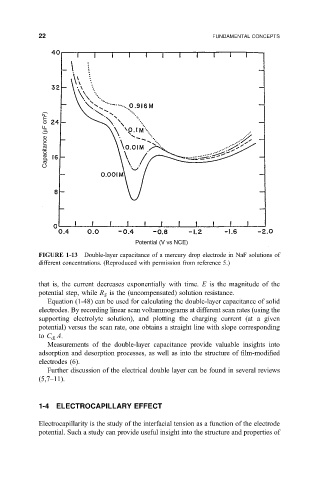
FIGURE 1-13 Double-layer capacitance of a mercury drop electrode in NaF solutions of
different concentrations. (Reproduced with permission from reference 5.)
that is, the current decreases exponentially with time. E is the magnitude of the
potential step, while R is the (uncompensated) solution resistance.
S
Equation (1-48) can be used for calculating the double-layer capacitance of solid
electrodes. By recording linear scan voltammograms at different scan rates (using the
supporting electrolyte solution), and plotting the charging current (at a given
potential) versus the scan rate, one obtains a straight line with slope corresponding
to C A.
dl
Measurements of the double-layer capacitance provide valuable insights into
adsorption and desorption processes, as well as into the structure of ®lm-modi®ed
electrodes (6).
Further discussion of the electrical double layer can be found in several reviews
(5,7±11).
1-4 ELECTROCAPILLARY EFFECT
Electrocapillarity is the study of the interfacial tension as a function of the electrode
potential. Such a study can provide useful insight into the structure and properties of