Page 29 - Analytical method for food addtives
P. 29
10
Reference
2
3
12
% square of correlation
(n=5)
(n=5)
(n=5)
(n=5)
ng
4
%
%
%
%
RSD 4.7
RSD 3.5
RSD 1.8
RSD 3.5
Determination limit
RSD 6.07
mg/L
mg/L
mg/L
mg/L
SD 5.5267
% for commercial samples
CV 3.5 %
mg/L
3.20
3.68
0.19
3.68
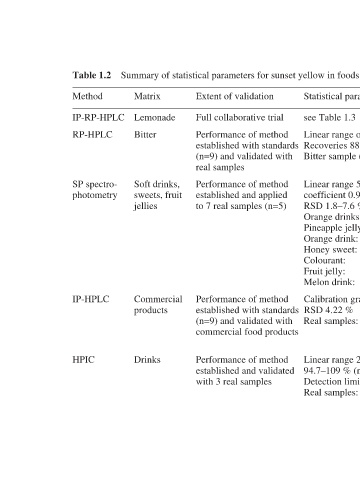
Bitter sample (n=9) see Table 1.4
Linear range of calibration 2–10
ng/mL
Recoveries 88.1–106.0 %
Statistical parameters Analytical methods for food additives (n=5) % RSD 2.5 mg/L 845.0 Colourant: (n=5) % RSD 7.6 mg/L 0.66 Fruit jelly: (n=5) % RSD 6.3 mg/L 23.60 Melon drink: 8 mg/L SD 0.071 mg/L Calibration graph linear from 2–10 % (n=5) Recovery 99.1 ng Detection limit 1.4 % RSD 4.22 mg/L 16.7±0.3 Bitter:
Linear range 50–650
coefficient 0.9977
Pineapple jelly:
Orange drinks:
Summary of statistical parameters for sunset yellow in foods
Orange drink:
Honey sweet:
see Table 1.3
RSD 1.8–7.6
Extent of validation Full collaborative trial Performance of method established with standards (n=9) and validated with real samples Performance of method established and applied to 7 real samples (n=5) Performance of method established with standards (n=9) and validated with commercial food products Performance of method est
Matrix Lemonade Bitter Soft drinks, sweets, fruit jellies Commercial products Drinks
Table 1.2 Method IP-RP-HPLC RP-HPLC SP spectro- photometry IP-HPLC HPIC