Page 130 - Antennas for Base Stations in Wireless Communications
P. 130
Antennas for Mobile Communications: CDMA, GSM, and WCDMA 103
dB[S(1,1)] dB[S(2,2)] dB[S(3,3)] dB[S(4,4)]
dB[S(5,5)] dB[S(6,6)] dB[S(7,7)] dB[S(8,8)]
−9.5 −9.5
−10 −10
−10.5 −10.5
−11 −11
−11.5 −11.5
−12 −12
dB −12.5 −12.5 dB
−13 −13
−13.5 −13.5
−14 −14
−14.5 −14.5
−15 −15
−15.5 −15.5
1.65 1.7 1.75 1.8 1.85 1.9 1.95 2 2.05 2.1 2.15 2.2
Frequency (GHz)
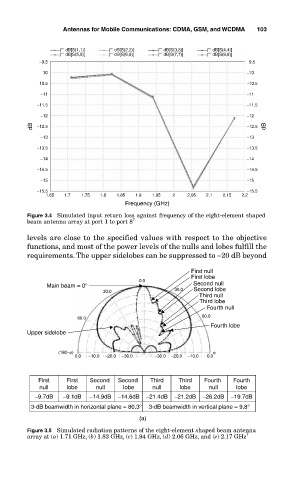
Figure 3.4 Simulated input return loss against frequency of the eight-element shaped
beam antenna array at port 1 to port 8 7
levels are close to the specified values with respect to the objective
functions, and most of the power levels of the nulls and lobes fulfill the
requirements. The upper sidelobes can be suppressed to −20 dB beyond
First null
First lobe
0.0
Main beam = 0° Second null
30.0 30.0 Second lobe
Third null
Third lobe
Fourth null
60.0 60.0
Fourth lobe
Upper sidelobe
(180–ϕ) ϕ
0.0 −10.0 −20.0 −30.0 −30.0 −20.0 −10.0 0.0
First First Second Second Third Third Fourth Fourth
null lobe null lobe null lobe null lobe
−9.7dB −9.1dB −14.9dB −14.6dB −21.4dB −21.2dB −26.2dB −19.7dB
3-dB beamwidth in horizontal plane = 80.3° 3-dB beamwidth in vertical plane = 9.8°
(a)
Figure 3.5 Simulated radiation patterns of the eight-element shaped beam antenna
array at (a) 1.71 GHz, (b) 1.83 GHz, (c) 1.94 GHz, (d) 2.06 GHz, and (e) 2.17 GHz 7