Page 146 - Antennas for Base Stations in Wireless Communications
P. 146
Antennas for Mobile Communications: CDMA, GSM, and WCDMA 119
R
R t
Y
Disc
X (φ = 0°)
Z
Circular patch Shorting
W 1 trapezoidal
plate
d t s
Z
t p
Disc t d X
H −Y
Wire h
GT
N-type
W 2 connector Ground plane
GR r
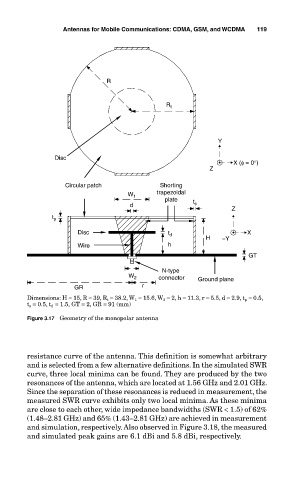
Dimensions: H = 15, R = 39, R t = 38.2, W 1 = 15.6, W 2 = 2, h = 11.3, r = 5.5, d = 2.9, t p = 0.5,
t s = 0.5, t d = 1.5, GT = 2, GR = 91 (mm)
Figure 3.17 Geometry of the monopolar antenna
resistance curve of the antenna. This definition is somewhat arbitrary
and is selected from a few alternative definitions. In the simulated SWR
curve, three local minima can be found. They are produced by the two
resonances of the antenna, which are located at 1.56 GHz and 2.01 GHz.
Since the separation of these resonances is reduced in measurement, the
measured SWR curve exhibits only two local minima. As these minima
are close to each other, wide impedance bandwidths (SWR < 1.5) of 62%
(1.48–2.81 GHz) and 65% (1.43–2.81 GHz) are achieved in measurement
and simulation, respectively. Also observed in Figure 3.18, the measured
and simulated peak gains are 6.1 dBi and 5.8 dBi, respectively.