Page 284 - Antennas for Base Stations in Wireless Communications
P. 284
Antennas for WLAN (WiFi) Applications 257
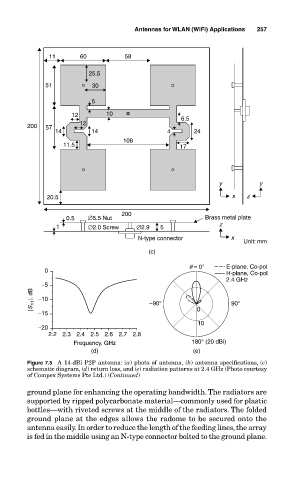
11 60 58
25.5
51 30
5
12 10 6.5
200 57 12
14 14 4 24
108
11.5 17
y y
20.5 x z
200
0.5 ∅5.5 Nut Brass metal plate
z
1 ∅2.0 Screw ∅2.9 5
N-type connector x
Unit: mm
(c)
q = 0° E-plane, Co-pol
0 H-plane, Co-pol
2.4 GHz
−5
|S 11 |, dB −10 −90° 90°
−15 0
10
−20
2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8
Frequency, GHz 180° (20 dBi)
(d) (e)
Figure 7.5 A 14-dBi P2P antenna: (a) photo of antenna, (b) antenna specifications, (c)
schematic diagram, (d) return loss, and (e) radiation patterns at 2.4 GHz (Photo courtesy
of Compex Systems Pte Ltd.) (Continued)
ground plane for enhancing the operating bandwidth. The radiators are
supported by ripped polycarbonate material—commonly used for plastic
bottles—with riveted screws at the middle of the radiators. The folded
ground plane at the edges allows the radome to be secured onto the
antenna easily. In order to reduce the length of the feeding lines, the array
is fed in the middle using an N-type connector bolted to the ground plane.