Page 201 - Applied Process Design For Chemical And Petrochemical Plants Volume III
P. 201
66131_Ludwig_CH10F 5/30/2001 4:35 PM Page 164
164 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
A number of obvious advantages and disadvantages exist
for either the horizontal or vertical thermosiphon reboiler.
For horizontal units, Yilmaz states that the TEMA types X, G,
and H shown in Figure 10-96C are in more common usage,
and types E and J are often used. The selection depends on
the heat transfer, fouling, and pressure drop on the shell
side. The X Shell is considered to have the lowest compara-
tive pressure drop, then H, G, and J, with E having the best
P. The circulation through the thermosiphon loop
described earlier depends on the pressure balance of the sys-
tem, including the static pressure of the liquid level and the
inlet pressure drop and exit two-phase pressure drops to and
from the reboiler, plus the pressure drop through the unit
itself.
Yilmaz 186 recommends that the maximum velocity in the
exit from the horizontal thermosiphon reboiler be the work
of Collins: 185
V max 77.15 1 tph 2 0.5 (10-138)
where
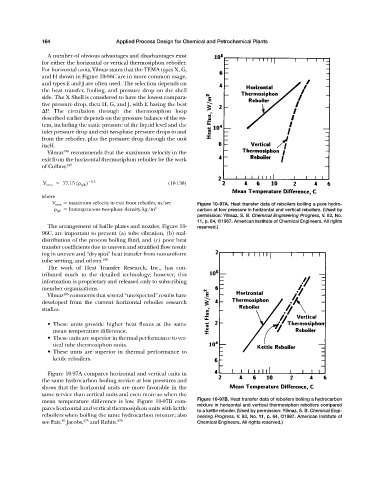
V max maximum velocity in exit from reboiler, m/sec Figure 10-97A. Heat transfer data of reboilers boiling a pure hydro-
tph homogeneous two-phase density, kg/m 3 carbon at low pressure in horizontal and vertical reboilers. (Used by
permission: Yilmaz, S. B. Chemical Engineering Progress, V. 83, No.
11, p. 64, ©1987. American Institute of Chemical Engineers. All rights
The arrangement of baffle plates and nozzles, Figure 10- reserved.)
96C, are important to prevent (a) tube vibration, (b) mal-
distribution of the process boiling fluid, and (c) poor heat
transfer coefficients due to uneven and stratified flow result-
ing in uneven and “dry spot” heat transfer from nonuniform
tube wetting, and others. 186
The work of Heat Transfer Research, Inc., has con-
tributed much to the detailed technology; however, this
information is proprietary and released only to subscribing
member organizations.
Yilmaz 186 comments that several “unexpected” results have
developed from the current horizontal reboiler research
studies.
• These units provide higher heat fluxes at the same
mean temperature difference.
• These units are superior in thermal performance to ver-
tical tube thermosiphon units.
• These units are superior in thermal performance to
kettle reboilers.
Figure 10-97A compares horizontal and vertical units in
the same hydrocarbon boiling service at low pressures and
shows that the horizontal units are more favorable in the
same service than vertical units and even more so when the
mean temperature difference is low. Figure 10-97B com- Figure 10-97B. Heat transfer data of reboilers boiling a hydrocarbon
mixture in horizontal and vertical thermosiphon reboilers compared
pares horizontal and vertical thermosiphon units with kettle
to a kettle reboiler. (Used by permission: Yilmaz, S. B. Chemical Engi-
reboilers when boiling the same hydrocarbon mixture; also neering Progress, V. 83, No. 11, p. 64, ©1987. American Institute of
46
see Fair, Jacobs, 273 and Rubin. 278 Chemical Engineers. All rights reserved.)