Page 348 - Applied Process Design For Chemical And Petrochemical Plants Volume III
P. 348
66131_Ludwig_CH11A 5/30/2001 4:49 PM Page 305
Refrigeration Systems 305
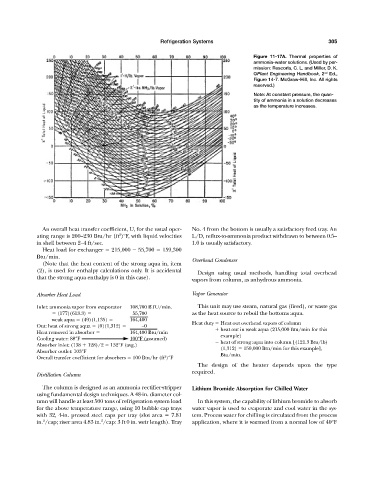
Figure 11-17A. Thermal properties of
ammonia-water solutions. (Used by per-
mission: Rescorla, C. L. and Miller, D. K.
©Plant Engineering Handbook, 2 nd Ed.,
Figure 14-7. McGraw-Hill, Inc. All rights
reserved.)
Note: At constant pressure, the quan-
tity of ammonia in a solution decreases
as the temperature increases.
An overall heat transfer coefficient, U, for the usual oper- No. 4 from the bottom is usually a satisfactory feed tray. An
2
ating range is 200—230 Btu/hr (ft )°F, with liquid velocities L/D, reflux-to-ammonia product withdrawn to between 0.5—
in shell between 2—4 ft/sec. 1.0 is usually satisfactory.
Heat load for exchanger 215,000 55,700 159,300
Btu/min.
Overhead Condenser
(Note that the heat content of the strong aqua in, item
(2), is used for enthalpy calculations only. It is accidental
Design using usual methods, handling total overhead
that the strong aqua enthalpy is 0 in this case).
vapors from column, as anhydrous ammonia.
Absorber Heat Load Vapor Generator
Inlet: ammonia vapor from evaporator 108,700 BTU/min. This unit may use steam, natural gas (fired), or waste gas
(177)(613.3) 055,700 as the heat source to reboil the bottoms aqua.
weak aqua (49)(1,135) 164,400
Out: heat of strong aqua (0)(1,312) –0 Heat duty Heat out overhead vapors of column
Heat removed in absorber 164,400 Btu/min heat out in weak aqua (215,000 Btu/min for this
example)
Cooling water: 88°F 100°F (assumed)
heat of strong aqua into column [(121.3 Btu/lb)
Absorber inlet: (138 128)/2 132°F (avg.)
(1,312) 159,000 Btu/min for this example],
Absorber outlet: 103°F
2
Overall transfer coefficient for absorbers 100 Btu/hr (ft )°F Btu/min.
The design of the heater depends upon the type
required.
Distillation Column
The column is designed as an ammonia rectifier-stripper Lithium Bromide Absorption for Chilled Water
using fundamental design techniques. A 48-in. diameter col-
umn will handle at least 500 tons of refrigeration system load In this system, the capability of lithium bromide to absorb
for the above temperature range, using 10 bubble cap trays water vapor is used to evaporate and cool water in the sys-
with 32, 4-in. pressed steel caps per tray (slot area 7.81 tem. Process water for chilling is circulated from the process
2
2
in. /cap; riser area 4.83 in. /cap: 3 ft 0 in. weir length). Tray application, where it is warmed from a normal low of 40°F