Page 349 - Applied Process Design For Chemical And Petrochemical Plants Volume III
P. 349
66131_Ludwig_CH11A 5/30/2001 4:49 PM Page 306
306 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
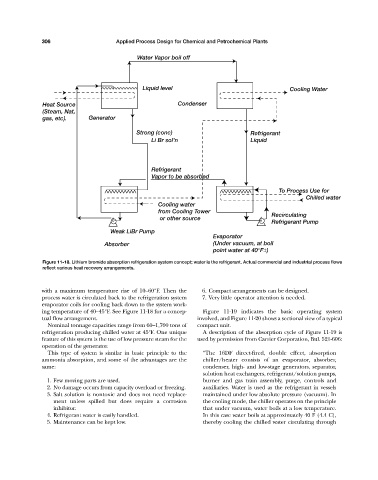
Water Vapor boil off
Liquid level Cooling Water
Heat Source Condenser
(Steam, Nat,
gas, etc). Generator
Strong (conc) Refrigerant
Li Br sol'n Liquid
Refrigerant
Vapor to be absorbed
To Process Use for
Chilled water
Cooling water
from Cooling Tower
Recirculating
or other source
Refrigerant Pump
Weak LiBr Pump
Evaporator
Absorber (Under vacuum, at boil
point water at 40°F±)
Figure 11-18. Lithium bromide absorption refrigeration system concept; water is the refrigerant. Actual commercial and industrial process flows
reflect various heat recovery arrangements.
with a maximum temperature rise of 10—60°F. Then the 6. Compact arrangements can be designed.
process water is circulated back to the refrigeration system 7. Very little operator attention is needed.
evaporator coils for cooling back down to the system work-
ing temperature of 40—45°F. See Figure 11-18 for a concep- Figure 11-19 indicates the basic operating system
tual flow arrangement. involved, and Figure 11-20 shows a sectional view of a typical
Nominal tonnage capacities range from 60—1,700 tons of compact unit.
refrigeration producing chilled water at 45°F. One unique A description of the absorption cycle of Figure 11-19 is
feature of this system is the use of low pressure steam for the used by permission from Carrier Corporation, Bul. 521-606:
operation of the generator.
This type of system is similar in basic principle to the “The 16DF direct-fired, double effect, absorption
ammonia absorption, and some of the advantages are the chiller/heater consists of an evaporator, absorber,
same: condenser, high- and low-stage generators, separator,
solution heat exchangers, refrigerant/solution pumps,
1. Few moving parts are used. burner and gas train assembly, purge, controls and
2. No damage occurs from capacity overload or freezing. auxiliaries. Water is used as the refrigerant in vessels
3. Salt solution is nontoxic and does not need replace- maintained under low absolute pressure (vacuum). In
ment unless spilled but does require a corrosion the cooling mode, the chiller operates on the principle
inhibitor. that under vacuum, water boils at a low temperature.
4. Refrigerant water is easily handled. In this case water boils at approximately 40 F (4.4 C),
5. Maintenance can be kept low. thereby cooling the chilled water circulating through