Page 150 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 150
136 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
Particle diameter
(largest 5%)
Tyler
mesh Inches Microns
8000 I
.250
6000
4 .185
4000
8 .093
2000
14 .W6
1000
800
28 .023 600
43 .012 400
200
100 .006
100
80
200 .003
325 .0017
40
1
HOMOGENEOUS
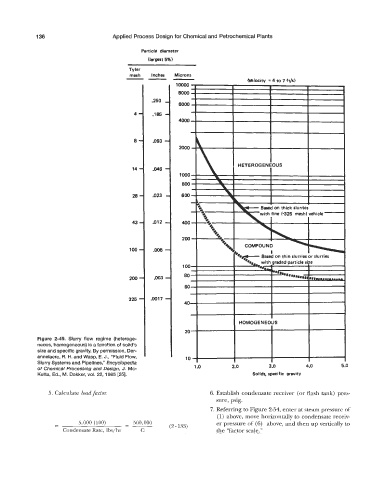
Figure 2-49. Slurry flow regime (heteroge-
neous, homogeneous) is a function of solid’s
size and specific gravity. By permission, Der-
annelaere, R. H. and Wasp, E. J., “Fluid Flow, 203 10
Slurry Systems and Pipelines,” Encyclopedia 1 .o 2.0 3.0 4.0 5 .O
of Chemical Processing and Design, J. Mc-
Ketta, Ed., M. Dekker, vol. 22, 1985 [25]. Solids, specific gravity
5. Calculate load factol: 6. Establish condensate receiver (or flash tank) pres-
sure, psig.
7. Referring to Figure 2-54, enter at steam pressure of
(1) above, move horizontally to condensate receiv-
- 5,000 (100) - 500,000 (2- 133) er pressure of (6) above, and then up vertically to
-
-___
Condensate Rate, Ibs/hr C the “factor scale.”