Page 158 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 158
NITROGEN
138
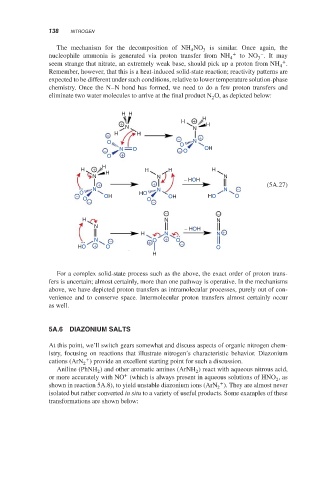
The mechanism for the decomposition of NH NO 3 is similar. Once again, the
4
–
nucleophile ammonia is generated via proton transfer from NH 4 + to NO .Itmay
3
+
seem strange that nitrate, an extremely weak base, should pick up a proton from NH .
4
Remember, however, that this is a heat-induced solid-state reaction; reactivity patterns are
expected to be different under such conditions, relative to lower temperature solution-phase
chemistry. Once the N–N bond has formed, we need to do a few proton transfers and
eliminate two water molecules to arrive at the final product N O, as depicted below:
2
HH H
+ H + H
N N
− H H +
O − N
O
− N O − O OH
O +
H + H H H H H
N N − HOH N
+ + (5A.27)
N N N −
− O OH HO OH HO O
O − O −
− −
H N N
N
− HOH
H N N +
N − + O + O
HO + O − O
H
For a complex solid-state process such as the above, the exact order of proton trans-
fers is uncertain; almost certainly, more than one pathway is operative. In the mechanisms
above, we have depicted proton transfers as intramolecular processes, purely out of con-
venience and to conserve space. Intermolecular proton transfers almost certainly occur
as well.
5A.6 DIAZONIUM SALTS
At this point, we’ll switch gears somewhat and discuss aspects of organic nitrogen chem-
istry, focusing on reactions that illustrate nitrogen’s characteristic behavior. Diazonium
+
cations (ArN ) provide an excellent starting point for such a discussion.
2
Aniline (PhNH ) and other aromatic amines (ArNH ) react with aqueous nitrous acid,
2
2
+
or more accurately with NO (which is always present in aqueous solutions of HNO ,as
2
+
shown in reaction 5A.8), to yield unstable diazonium ions (ArN ). They are almost never
2
isolated but rather converted in situ to a variety of useful products. Some examples of these
transformations are shown below: