Page 161 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 161
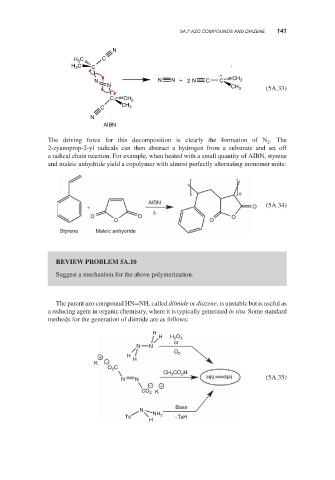
5A.7 AZO COMPOUNDS AND DIAZENE 141
N
H 3 C C
H 3 C C
N N N + 2 N C C CH 3
N CH 3 (5A.33)
C CH 3
C CH 3
N
AIBN
The driving force for this decomposition is clearly the formation of N .The
2
2-cyanoprop-2-yl radicals can then abstract a hydrogen from a substrate and set off
a radical chain reaction. For example, when heated with a small quantity of AIBN, styrene
and maleic anhydride yield a copolymer with almost perfectly alternating monomer units:
n
AIBN
+ O (5A.34)
Δ
O O O
O O
Styrene Maleic anhydride
REVIEW PROBLEM 5A.10
Suggest a mechanism for the above polymerization.
The parent azo compound HN=NH, called diimide or diazene, is unstable but is useful as
a reducing agent in organic chemistry, where it is typically generated in situ. Some standard
methods for the generation of diimide are as follows:
H
H H 2 O 2
or
N N
O 2
+ H
K − H
O 2 C
CH 3 CO 2 H
HN NH (5A.35)
N N
− +
K
CO 2
Base
N
Ts NH 2 −TsH
H