Page 164 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 164
NITROGEN
144
5A.8* IMINES AND RELATED FUNCTIONAL GROUPS: THE
WOLFF–KISHNER REDUCTION AND THE SHAPIRO REACTION
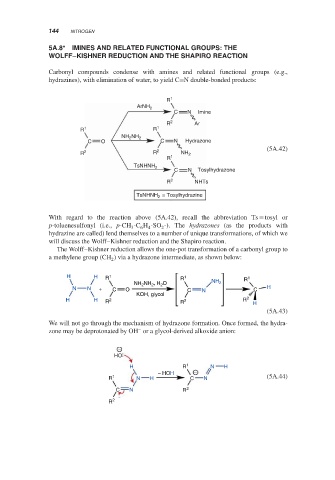
Carbonyl compounds condense with amines and related functional groups (e.g.,
hydrazines), with elimination of water, to yield C=N double-bonded products:
R 1
ArNH 2
C N Imine
R 2 Ar
R 1 R 1
NH NH 2
2
C O C N Hydrazone
(5A.42)
R 2 R 2 NH 2
R 1
TsNHNH 2
C N Tosylhydrazone
R 2 NHTs
= Tosylhydrazine
TsNHNH 2
With regard to the reaction above (5A.42), recall the abbreviation Ts = tosyl or
p-toluenesulfonyl (i.e., p-CH -C H -SO -). The hydrazones (as the products with
3
2
4
6
hydrazine are called) lend themselves to a number of unique transformations, of which we
will discuss the Wolff–Kishner reduction and the Shapiro reaction.
The Wolff–Kishner reduction allows the one-pot transformation of a carbonyl group to
a methylene group (CH ) via a hydrazone intermediate, as shown below:
2
H H R 1 R 1 R 1
NH NH , H O NH 2
2
2
2
N N + C O C N C H
KOH, glycol
H H R 2 R 2 R 2 H
(5A.43)
We will not go through the mechanism of hydrazone formation. Once formed, the hydra-
–
zone may be deprotonated by OH or a glycol-derived alkoxide anion:
−
HO
H R 1 N H
− HOH −
R 1 N H C N (5A.44)
C N R 2
R 2