Page 169 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 169
5A.10 NITRENES AND NITRENOIDS: THE CURTIUS REARRANGEMENT 149
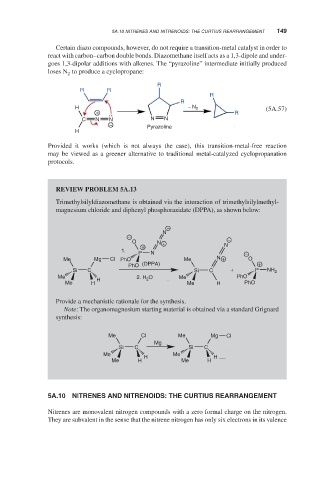
Certain diazo compounds, however, do not require a transition-metal catalyst in order to
react with carbon–carbon double bonds. Diazomethane itself acts as a 1,3-dipole and under-
goes 1,3-dipolar additions with alkenes. The “pyrazoline” intermediate initially produced
loses N to produce a cyclopropane:
2
R
R R
R
R
H − N 2 (5A.57)
+ R
C N N N N
− Pyrazoline
H
Provided it works (which is not always the case), this transition-metal-free reaction
may be viewed as a greener alternative to traditional metal-catalyzed cyclopropanation
protocols.
REVIEW PROBLEM 5A.13
Trimethylsilyldiazomethane is obtained via the interaction of trimethylsilylmethyl-
magnesium chloride and diphenyl phosphorazidate (DPPA), as shown below:
−
N
− −
O N +
+ N
1.
P N −
Me Mg Cl PhO Me N + O
PhO (DPPA) +
Si C Si C + P NH 2
Me H 2. H O Me PhO
2
Me H Me H PhO
Provide a mechanistic rationale for the synthesis.
Note: The organomagnesium starting material is obtained via a standard Grignard
synthesis:
Me Cl Me Mg Cl
Mg
Si C Si C
Me H Me H
Me H Me H
5A.10 NITRENES AND NITRENOIDS: THE CURTIUS REARRANGEMENT
Nitrenes are monovalent nitrogen compounds with a zero formal charge on the nitrogen.
They are subvalent in the sense that the nitrene nitrogen has only six electrons in its valence