Page 173 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 173
5A.11 NITRIC OXIDE AND NITROGEN DIOXIDE 153
The N–N bond in N O is long (1.78 Å, compared with 1.49 Å for hydrazine) and weak,
4
2
and ΔH for the above dimerization is only about –57.2 kJ/mol. Thus, NO is favored at
2
higher temperatures whereas N O predominates at lower temperatures.
4
2
Nitrogen dioxide reacts with water to yield a mixture of nitrous and nitric acids:
2NO + H O → HNO + HNO 3 (5A.68)
2
2
2
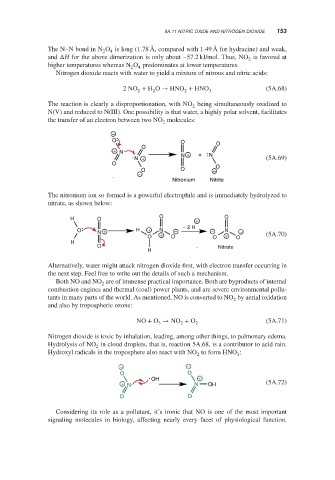
The reaction is clearly a disproportionation, with NO being simultaneously oxidized to
2
N(V) and reduced to N(III). One possibility is that water, a highly polar solvent, facilitates
the transfer of an electron between two NO molecules:
2
−
O O O
O
+ N N + +
N + N (5A.69)
O O
O O −
−
Nitronium Nitrite
The nitronium ion so formed is a powerful electrophile and is immediately hydrolyzed to
nitrate, as shown below:
O O
H O +
O N + H + N − − 2 H − N −
O + O O + O (5A.70)
H
O Nitrate
H
Alternatively, water might attack nitrogen dioxide first, with electron transfer occurring in
the next step. Feel free to write out the details of such a mechanism.
Both NO and NO are of immense practical importance. Both are byproducts of internal
2
combustion engines and thermal (coal) power plants, and are severe environmental pollu-
tants in many parts of the world. As mentioned, NO is converted to NO by aerial oxidation
2
and also by tropospheric ozone:
NO + O → NO + O (5A.71)
3 2 2
Nitrogen dioxide is toxic by inhalation, leading, among other things, to pulmonary edema.
Hydrolysis of NO in cloud droplets, that is, reaction 5A.68, is a contributor to acid rain.
2
Hydroxyl radicals in the troposphere also react with NO to form HNO :
2 3
− −
O O
OH +
+ N N OH (5A.72)
O O
Considering its role as a pollutant, it’s ironic that NO is one of the most important
signaling molecules in biology, affecting nearly every facet of physiological function.