Page 177 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 177
THE HEAVIER PNICTOGENS 157
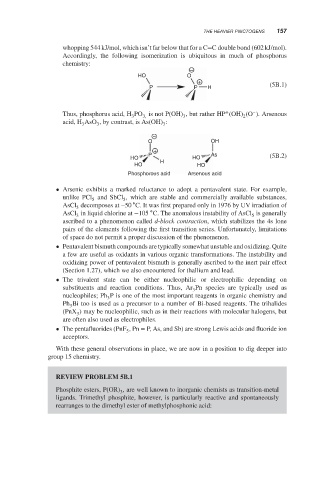
whopping 544 kJ/mol, which isn’t far below that for a C=C double bond (602 kJ/mol).
Accordingly, the following isomerization is ubiquitous in much of phosphorus
chemistry:
−
HO O
+
P P H (5B.1)
+ –
Thus, phosphorus acid, H PO is not P(OH) , but rather HP (OH) (O ). Arsenous
3
3,
2
3
acid, H AsO , by contrast, is As(OH) :
3
3
3
−
O OH
+
P As
HO HO (5B.2)
H
HO HO
Phosphorous acid Arsenous acid
• Arsenic exhibits a marked reluctance to adopt a pentavalent state. For example,
unlike PCl and SbCl , which are stable and commercially available substances,
5
5
∘
AsCl decomposes at –50 C. It was first prepared only in 1976 by UV irradiation of
5
∘
AsCl in liquid chlorine at −105 C. The anomalous instability of AsCl is generally
3
5
ascribed to a phenomenon called d-block contraction, which stabilizes the 4s lone
pairs of the elements following the first transition series. Unfortunately, limitations
of space do not permit a proper discussion of the phenomenon.
• Pentavalent bismuth compounds are typically somewhat unstable and oxidizing. Quite
a few are useful as oxidants in various organic transformations. The instability and
oxidizing power of pentavalent bismuth is generally ascribed to the inert pair effect
(Section 1.27), which we also encountered for thallium and lead.
• The trivalent state can be either nucleophilic or electrophilic depending on
substituents and reaction conditions. Thus, Ar Pn species are typically used as
3
nucleophiles; Ph P is one of the most important reagents in organic chemistry and
3
Ph Bi too is used as a precursor to a number of Bi-based reagents. The trihalides
3
(PnX ) may be nucleophilic, such as in their reactions with molecular halogens, but
3
are often also used as electrophiles.
• The pentafluorides (PnF ,Pn = P, As, and Sb) are strong Lewis acids and fluoride ion
5
acceptors.
With these general observations in place, we are now in a position to dig deeper into
group 15 chemistry.
REVIEW PROBLEM 5B.1
Phosphite esters, P(OR) , are well known to inorganic chemists as transition-metal
3
ligands. Trimethyl phosphite, however, is particularly reactive and spontaneously
rearranges to the dimethyl ester of methylphosphonic acid: