Page 181 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 181
5B.2 HALIDES AND OXOHALIDES 161
P
P P
+
Cl Cl P P Cl P
P P P Cl
− P
P Cl P
Cl
(5B.8)
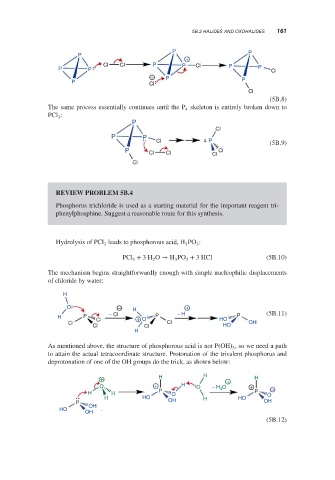
The same process essentially continues until the P skeleton is entirely broken down to
4
PCl :
3
P
Cl
P P
Cl 4 P (5B.9)
P Cl Cl Cl Cl
Cl
REVIEW PROBLEM 5B.4
Phosphorus trichloride is used as a starting material for the important reagent tri-
phenylphosphine. Suggest a reasonable route for this synthesis.
Hydrolysis of PCl leads to phosphorous acid, H PO :
3 3 3
PCl + 3H O → H PO + 3 HCl (5B.10)
3
2
3
3
The mechanism begins straightforwardly enough with simple nucleophilic displacements
of chloride by water:
H
O − H +
H P Cl − Cl + O P − H HO P (5B.11)
Cl Cl OH
Cl Cl HO
H
As mentioned above, the structure of phosphorous acid is not P(OH) , so we need a path
3
to attain the actual tetracoordinate structure. Protonation of the trivalent phosphorus and
deprotonation of one of the OH groups do the trick, as shown below:
+ H H + H
O + H O − H O + −
3
H H P O P O
H HO H HO
P OH OH
OH
HO
OH
(5B.12)